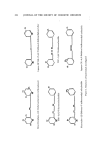
PERCUTANEOUS ABSORPTION OF DRUGS 383 Thus, it appears that the lower vasoconstriction activity of the acetates is primarily due to their poor water solubility. When Taft's polar substituent constant o'* of the 6-a substituent is included, significant improvement in correlation is obtained (eq 34, F•,5 = 13.8 F1,5o.9•5= 10.0). This suggests that while partition is important for the penetration of the steroids into the epidermis, the electronic property as represented by the o'* of the 6-a sub- stituent may be important in the drug-receptor interaction to produce the observed vasoconstriction effect. We have also explored Taft's steric param- eter E8 (21) of the 6-a substituent, and the E8 and o'* of the 9-a substituent none of these terms improves the correlation significantly. CONCLUSION From the results obtained it appears that the lipophilic character of the compound, as measured by partition coefficient, plays the most important role in determining percutaneous absorption. In addition to this, when the solubility in water is very low, it may impose another limiting factor. Electronic and steric terms appear to play minor roles in the series of com- pounds examined. It is encouraging to see that percutaneous absorption of various types of compounds can be correlated with physicochemical proper- ties of the causative agents. ACKNOWLEDGiV•ENT The authors wish to thank the Computer Science Laboratories of the Uni- versity of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, for data processing. (Received June 7, 1972) REFERENCES (1) Blank, I. H., Mechanism of percutaneous adsorption: The effect of temperature on the transport of non-electrolytes across the skin. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 11, 57 (1960). (2) Harry, R. G., Modern Cosmeticology, Vol. 12, Leonard Hill, Ltd., London, 1962, Chap. 3. (3) Sagarin, E., Cosmetics, Science and Technology, Interscience Publisher, Inc., New York, 1957, pp. 1156-60. (4) Lien, E. J., Koda, R. T., and Tong, G. L., Buccal and percutaneous absorptions, Drug. Intell., 5, 38 (1971). (5) Fujita, T., Iwasa, J., and Hansch, C., A new $ubstituent constant, pi, derived from partition coefficients, 1. Amer. Chem. Soc., 86, 5175 (1964). (6) Iwasa, J., Fuiita, T., and Hansch, C., Substituent constants for aliphatic functions obtained from partition coefficients, 1. Med. Chem., 8, 150 (1965). (7) Lien, E. J., The use of substituent constants and regression analysis in the study of structure-activity relationship, Amer. 1. Pharm. Educ., 33, 368 (1969). (8) Hansch, C., A quantitative approach to biochemical structure-activity relationships, Accounts Chem. Res., 2, 232 (1969). (9) Hansch, C., Steward, A. R., and Iwasa, J., The correlation of localization rates of benzeneboronic acids in brain and tumor tissue with sustituent constants, Mol. Pharmacol., 1, 87 (1965).
384 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) (18) (19) (20) (.•1) Clendenning, W. E., and Stoughton, R. R., Importance of the aqueous/lipid parti- tion coeffcient for percutaneous absorption of weak electrolytes, J. Invest. Dermatol., 39, 47 (1962). Shriner, R. L., Fuson, R. C., and Curtin, D. Y., The S[tstematic Identification o[ Organic Compounds, 4th ed., J. Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1956, p. 50. Treherne, J. E., The permeability of skin to some non-electrolytes, J. Ph[tsiol., 133, 171 (1956). Leo, A., Hansch, C., and Elkins, D., Partition coefficients and their uses, Chem. Rev., 71, 525 (1971). Scheuplein, R. J., Mechanism of percutaneous absorption. I. Routes of penetration and the influence of solubility, J. Invest Dermatol., 45, 334 (1966). Scheuplein, R. J., et al., Percutaneous absorption of steroids, Ibid., 52, 63 (1969). Flynn, G. L., Structural approach to partitioning: Estimation of steroid partition coef- ficients based upon molecular constitution, J. Pharm. Sci., 60, 345 (1971). Stoughton, R. B., Clendenning, W. E., and Lruse, D., Percutaneous absorption of nicotinic acid and derivatives, J. Invest. Dermatol., 35, 337 (1960). Katz, M., and Shaikh, Z. 1., Percutaneous corticosteroid absorption correlated to par- tition coeffcient, J. Pharm. Sci., 54, 591 (1965). Dixon, W. J., Biomedical Computer P•ograms, University of California Press, Berke- ley, 1971, pp. 215-58. Kuo, S.S., Numerical Methods and Computers, Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Reading, Mass., 1965, Chap. 11. Lefller, J. E., and Grunxvald, E., Rates and Equilibria o[ Organic Reactions, John Wiley, New York, 1963.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)