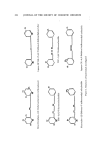
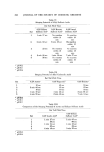
IRRITANCY AND STINGING POTENTIAL 389 Table IV Stinging Potential of 0.3N Acetic Acid Rat Tail Flick Time Rat 1 2 3 1 3 min 27 sec 1 min 20 see 4 min 05 sec 2 No reaction No reaction No reaction within 10 within 10 within 10 min rain min 3 30 sec i min 40 sec 1 rain 45 sec 4 i rain 15 sec 2 min 17 sec 1 min 26 sec 5 40 sec I min 18 sec 1 min 18 sec Table V Stinging Potential of 0.3N Hexane Sulfonic Acid Rat Tail Flick Time Rat 1 2 3 i 3 min 16 sec 3 rain 08 sec 3 min 22 sec 2 34 sec 36 sec 40 sec 3 4 min 44 sec 2 min 47 sec 1 rain 34 sec 4 No reaction No reaction No reaction within 10 within 10 within 10 rain rain rain 5 2 rain 02 sec 2 min 22 sec 2 rain 22 sec single animal, we have chosen to consider only appreciable differences in threshold times as indicative of real differences in stinging potential. In order to conapare animal test results with those obtained on humans, the stinging potential of ethane, hexane, and lauryl sulfonic acids were inter- compared (Table VI). Agreement with human results appears fairly good. Also, as in results with humans, stinging was not related to the pH of the solution. ,, The stinging potential of a series of alkyl carboxylic acids was next eval- uated (Table VII). No consistent differences in stinging could be discerned among the acids tested. (All seemed to produce a high level of sting.) How- ever, it should be noted that tl•e differences between the carboxylie acids in terms of alkyl lengths were not as pronounced as with the sulfonic acids. The limited solubility of the longer-chain carboxylic acids prevented their inclu- sion for testing. When ethane sulfonic acid was compared directly to acetic acid in terms of stinging potential, both were found to be equally stinging in spite of relative- ly large differences in pH of the solutions (Table VIII). The effect of altering the ratio of methylene to carboxyl groups on stinging xvas further studied using a homologous series of dicarboxylic acids (Table IX). While the results are not conclusive, they do suggest that the added
390 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table VI Stinging Potential of Alkyl Sulfonic Acids Rat Tail Flick Time 0.3N Ethane 0.3N Hexane 0.3N Lauryl Rat Sulfonic Acid • Sulfonic Acid"Sulfonic Acid ø i I min 17 sec No reaction No reaction within 10 within 10 min min 2 2 rain 30 sec 5 •nin 40 sec No reaction within 10 min 3 23 sec No reaction No reaction within 10 within 10 min min 4 2 min 08 sec i min 30 sec 7 min 57 sec 5 36 sec No reaction No reaction within 10 within 10 min •nin • pH 0.8. b pH 0.7. o pH O.9. Table VII Stinging Potential of Alkyl Carboxylic Acids Rat Tail Flick Time Rat 0.3N Acetic a 0.3N Propronic * 0.3N Butyric ø I 10 sec 45 sec 16 sec 2 2 min 06 sec 15 sec 15 sec 3 10 sec 10 sec 10 sec 4 1 min 10 see 1 min 43 see 5 rain 51 sec 5 4 min 58 sec 6 min 42 sec 7 rain 14 sec ø pH 9..6. * pH 2.7. • pH 2.7. Table VIII Comparison of the Stinging Potential of Acetic and Ethane Su]fonic Acids Rat Tail Flick Time 0.3N Ethane Rat 0.3N Acetic Acid • Sulfonic Acid * 1 1 rain 27 sec 1 min 05 sec 2 55 see 60 sec 3 1 rain 04 see 1 rain 42 see 4 05 sec 39 sec 5 4 min 40 sec 3 min 50 sec "pH 2.6. b pH 0.8.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)