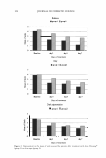
2005 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 201 BOTANICALS FROM TR ADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE (TCM) AND THEIR POTENTIAL AS NATURAL ANTI-IRRITANTS IN COSMETIC APPLICATIONS Gabriele Vielhaber, Ph.D., Imke Meyer, Holger Joppe, Helge Franke and Martina Herrmann, Ph.D. Symrise GmbH & Co. KG, Muhlenfeldstr. 1, D-37603, Holzminden, Germany Introduction Many plants are known that are traditionally used for their anti-inflammatory activity. In most cases, the evidence for the anti-inflammatory activity is derived from animal models or immunocompetent cells but efficacy proof on human skin cells is scarce. In skin, interleukin-I (IL-la) is a key mediators in the inflammatory process. Increased cutaneous levels of IL-la are found in conditions with a weakened epidermal barrier such as aged skin, dry skin or sensitive skin as well as in photodamaged skin [1-4]. However, specific IL-la inhibitors are rare. We have evaluated the IL-la inhibitory efficacy of plant extracts from traditional chinese medicine (TCM) on human keratinocytes. Since reactive oxygen species are a major trigger in the inflammatory cascade, we have also investigated whether the radical scavenging activity of the extracts significantly contributes to their anti-irritant activity. Materials and Methods IL- I a Assay: HaCaT keratinocytes were seeded into 96well microplates and grown to 90-100 % confluency. The medium was exchanged against solutions containing the test compounds. After 1 h, IL-Ia biosynthesis was stimulated by addition of 0.4 µM A23187 (Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany). After a further 6 h, the cells were lysed with 1 % Triton X 100 in PBS and the IL-Ia content was measured with the Human IL-la ELISA Kit from Perbio Science (Bonn, Germany). Oexamethasone was used as a reference (1 µM = 43% IL-la inhibition). LOH Assay: Lactate dehydrogenase (LOH) activity in the supernatant was determined by use of the Cytotoxicity Detection Kit from Roche (Mannheim, Germany). ABTS Assay: Samples were incubated for 10 min at 30°C with the 2,2'-Azino}!is-(3-ethylbenzo!hiazoline-6- §.Ulfonate (ABTS) radical cation which was prepared by reaction of ABTS with potassium persulfate. The degree of decolorization corresponds to the radical scavenging activity and was determined spectrophotometrically at 734 nm . Results and Discussion For measurement of IL-la the human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT was used since these cells were easier to handle than primary keratinocytes. To assure that the enhanced levels of IL- I a were not due to cytotoxicity, a LDH assay with the supernatant was performed in parallel to the anti-irritant assay. Japanese honeysuckle flowers (Lonicera japonica), kudzu roots (Pueraria lobata) and Japanese pagoda tree flowers (Sophorajaponica) were found to possess considerable anti-irritant activity. At 1 %, the extract preparations containing 3% of dry extract (trade name: Extrapone®) inhibited IL-la by 40 % (Honeysuckle) and 29 % {Pueraria, Sophora), respectively. Additionally, 0.1 % of the extracts also exhibited potent radical scavenging capacity in the cell-free ABTS assay with a maximum antioxidant capacity of 25 % (Honeysuckle), 81 % (Pueraria) and 22 % {Sophora), respectively. To elucidate the respective active principles of the TCM extracts, phytochemical characterization was performed by HPLC-OAD-MS analysis. As major UV-detectable components chlorogenic acid (0.08%), puerarin (0.17%), and rutin {0.10%), respectively were identified. However, the anti-irritant and radical scavenging activity of the single compounds and the extracts did not correlate. Only in the case of Sophora the radical scavenging activity could be fully ascribed to its major component rutin.
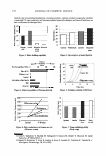
202 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE o_ i� •- II .Cl .c :c.e .E II 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% • '";- 15% = 10% 5% 0% 1 % Extrapone Honeysuckle (0.0008% Ollorogenic acid*) 1 % Extrapone A.leraria (0.0017% A.lerarin*) 1 % Extrapone Sophora (0.00103% Rutin*) * Concentration of the major component in 1.0 % Extrapone Figure 1: IL-I alpha inhibition ofTCM Extracts and the respective major components. 90% 0% 0.1 % Exlrapone Honeysuckle (0.00008% Chlorogenic acid*) 0.1% Exlrapone Pueraria (0.00017% Puerarin*) 0.1% Exlrapone Sophora (0.000103% Rutin*) * Concentration of the major component in 0.1 % Extrapone Figure l: Antioxidant capacity ofTCM Extracts and the respective major components. Conclusion Extracts from the TCM plants Japanese honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica), kudzu (Pueraria /obata) and Japanese pagoda tree (Sophora japonica) exhibit potent anti-irritant activity in human epidermal keratinocytes. The anti- irritant activity of these extracts does not correlate with their radical scavenging activity. Moreover, only a small part of the anti-irritant and anti-oxidant activity of the extracts could be ascribed to the respective major ingredients. Thus, the presence of several ingredients in a botanical extract is apparently essential for optimal efficacy. References [I) Ye, J., Garg, A., Calhoun, C., Feingold K.R., Elias, P.M., and Ghadially, R. Exp. Dermato/. 11, 209-16 (2002) [2] zur Muhlen, A., Klotz, A., Weimans, S., Veeger, M., Thomer, B., Diener, B., and Hermann. M. Skin Pharmaco/. Physiol. 17, 167-75 (2004) [3] Ashida, Y., M. Ogo and M. Denda Br. J. Dermatol. 144, 238-43 (2001) [4) Seo J.Y., Kim E.K., Lee S.H., Park K.C., Kim K.H., and Chung J.H. Mech. Ageing Dev. 124, 903-10 (2003)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)