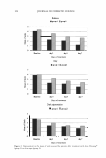
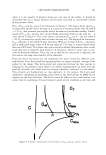
2005 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 185 NANO-SIZED HYBRID CAPSULES BASED ON CYCLODEXTRIN ESTERS: A TOTALLY NEW FLUIDIC ORGANIZATION FOR PENETRATION ENHANCEMENT OF COSMETIC ACTIVE COMPOUNDS Janice Hart*, Delphine Rival', N. Terry2, S. Bonnett, C. Buffevant1 and E. Perrier 1 1 Engelhard-Lyon, 32 Rue St. Jean de Dieu, F-69366, Lyon, France 2 /BCP, CNRS UPR 412, Impasse du Vercors, 69367, Lyon, France delphine. rival@engelhard.com *Janice Hart is presenting on behalf of Engelhard-Lyon Nanotechnologies promised for human being future, a better life as far as health management and medical applications are concerned. Cosmetic companies have been, in this area, one step ahead and have already developed fantastic applications using nanocapsules or nanospheres that are not yet used in the pharmaceutical area. The aim of our study was to develop a chemically modified cyclodextrin that would be able to associate spontaneously into nano-size range biovector, able to mimic the fluidic membrane of liposomes, and able to stimulate the penetration of encapsulated active compounds. The concept of this development was linked with the idea that such type of biovector would induce a double encapsulation system, the encapsulated active compounds being both in the cavity of the cyclodextrin and inside the nanoparticle formed with those nanostructures as well. The tluidic membrane of this biovector enhances the penetration ability. Methods and Results: Progressive chemical esterification was employed using 3 to 15 equivalent of )auric fatty chains for one equivalent of beta-cyclodextrin. Nanoparticles were produced using the solvent evaporation technique. They were analysed for their size (N4 Plus, Beckman Coulter), their shape (using Atomic Force Microscopy, Explorer Thermomicroscope) and for their encapsulated active compounds using conventional HPLC techniques. Penetration of encapsulated active compounds (catechol, 0.1 %, p/p) between those structures (called CYCLOCAPS®, Engelhard, Lyon, France), was then compared with a solution of free catechol and standard liposomes, using Franz cell diffusion devices and rat skin biopsies. Diffusion of each product was estimated at 5, IO and 24 hours by measuring fluorescence (276/298) in the medium in the lower compartment of the Franz cell constituted by PBS with ethanol 80/20. Comparison or the diffusion or catechol in its rree and liposorne forms and encapsulated in CYCLOCAPS Tlrre (hours) Cyclocaps 24H: • statistically different (p0.05) from free form ,.,. statistically different (p0.01) from liposome form Cyclocaps I OH: *"' statistically different (p0.01) from liposome form Cyclocaps 5H: *statistically different (p0.05) from liposome form
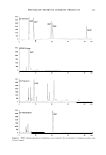
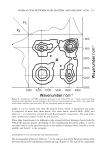
186 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Trans-cutaneous penetration studies have shown that this new biovector induces a very good penetration of active compounds inside the deep part of the skin, which is a property particularly interesting for substances developed for instance for their ability to promote extracellular matrix synthesis, or to inhibit MMPs or tyrosinase activities. Moreover, for the active compounds that have been tested during these studies, penetrations were far above the ones obtained with standard liposomes, which makes those fluidic nanoparticles very interesting for their cosmetic activities. Observations of those nanoparticules were also performed into suspension using fluorescent microscopy (Axioskop2+, Zeiss), with a rhodamine filter (546/590), after encapsulation of Octadecyl Rhodamine (Molecular probes, USA). The particle size last from 100 to 300 nm according to the nature of the active compound that is encapsulated. The stability of size and shape has been controlled into suspension for more than 2 years. Mathematical modelisation was performed using advanced modelisation computer models using Turbo-Frodo software and docking experiments to evaluate the complex hybrid structure organisation of such capsule membranes. Encapsulation of different active compounds performed: vitamins (B6, B3, H, B12, B2, A and E), slimming products such as caffeine, theophyllin, carnitine, and Centella Asiatica extract: antioxidants such as ubiquinones and whitening products such as catechol or lipoic acid. Conclusion and penpeetives These new tluidic and fractal nanosized vectors allow an improved performance of encapsulated active compounds devoted for the deeper part of the skin, without providing any side effect. It is a safe biovector, and allows some real breakthrough in the Nanotechnology field that induces a complete modification in the usual classification of nano-biovectors. The next evolution of those biovectors will be around cell targeting, which could be made by grafting some chemical structures with cell membrane affinities, onto the structure of those nanoparticles
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)