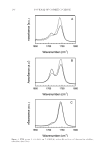
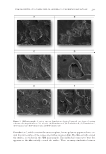
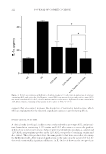
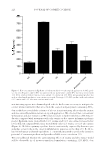
STUDIES OF CAFFEINE-LOADED SOLID LIPID NANOPARTICLES 173 (18) H. Hamishehkar, S. Same, K. Adibkia, K. Zarza, J. Shokri, M. Taghaee, and M. Kouhsoltani, A com- parative histological study on the skin occlusion performance of a cream made of solid lipid nanoparti- cles and vaseline. Res. Pharm. Sci., 10(5), 378–387 (2015). (19) M. Schneider, F. Stracke, S. Hansen, and U. F. Schaefer, Nanoparticles and their interactions with the dermal barrier. Dermatoendocrinol., 1(4), 197–206 (2009). (20) C. H. Liu, C. T. Wu, and J. Y. Fang, Characterization and formulation optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles in vitamin K1 delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 36(7), 751–61 (2010). (21) R. M. Khalil, A. A. El-Bary, M. A. Kassem, M. M. Ghorab, and M. Basha, Infl uence of formulation parameters on the physicochemical properties of meloxicam-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Egypt Pharmaceut. J., 12, 63–72 (2013). (22) R. Shah, D. Eldridge, E. Pal ombo, and I. Harding, Optimisation and stability assessment of solid lipid nanoparticles using particle size and zeta potential. Int. J. Phys. Sci., 25, 59–75 (2014). (23) F. G. Yener and M. Uner, Imp ortance of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in various administration routes and future perspectives. Int. J. Nanomedicine, 2, 289–300 (2007). (24) P. Costa and J. M. S. Lobo, Modeling and comparison of dissolution profi les. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 13, 123–133 (2001).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)