TAURINE/ALOE VERA FOR BOOSTING ANTI-SKIN IRRITATION EFFECTS 215 percutaneous absorption of taurine with or without the addition of aloe extract in vitro. EpiDerm human skin model was also used to measure the release of infl ammatory cyto- kines and chemokines, such as IL-1α and IL-8, to assess for skin irritation in vitro. To confi rm in vitro results, a human in vivo study was conducted to assess skin irritation after the topical application of prototype AlCl3 products containing taurine and aloe extract. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS AND FORMULATION The compounds tested in these experiments were acquired from a variety of vendors that are listed as follows: Hexaaqua 99.5% Aluminum Chloride Hexahydrate (Alfa Aesar, Ward Hill, MA), Aloe Vera Freeze Dried Powder 200× (Mexi Aloe, Campeche, Mexico), and Taurine 99% (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). AlCl3, aloe vera extract, and taurine (w/w) solutions were prepared by dissolving compounds into phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution pH 7.4 (Life Technologies, Merelbeke, Belgium). Final solutions were prepared by combining 0.5 ml of AlCl3 solution and 0.5 ml aloe extract and/or taurine solutions. Aqueous solutions of AlCl3 for initial irritation testing had 14% (w/w) AlCl3 concentration. The initial concentration of 14% AlCl3 was selected to induce high levels of irritation to observe signifi cant differences after the addition of anti-irritating actives, taurine and aloe extract. Subsequent sets of experiments had 12% AlCl3 concentration because the commercial product selected for irritation testing contains 12% AlCl3 as ac- tive concentration. Prototype products containing 12% AlCl3 (w/w) were oil-in-water emulsion formulations. EPIDERMIS MODEL The EpiDerm skin model (SIT-200 skin irritation model, MatTek Corporation, Ashland, MA) is a multilayered, highly differentiated model of the human epidermis composed of normal, human epidermal keratinocytes. EpiDerm consists of organized layers analogous to in vivo epidermis. It contains the basal, spinous, granular, and cornifi ed layers that are found in vivo. The EpiDerm tissue are cultured on cell culture inserts and shipped in a 24-well plate on agarose. The manufacturer ships PBS solution and culture media made specifi cally for the EpiDerm tissue. On arrival, tissue inserts were removed and placed onto 1.0 ml of culture medium for 24 h before testing. MTT CELL CYTOTOXICITY ASSAY Cytotoxicity was evaluated by mitochondrial metabolic activity using 3-[4,5-dimethyl- thiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich) MTT-reduction assay. In this study, a modifi ed method of MTT assay was used. MTT solution was prepared as 1.0 mg/ml in PBS prior to usage. After treating tissues with test products by follow- ing the protocol described previously, MatTek EpiDerm tissue were placed in a 24-well tissue culture plate 24 h after treatment and 500 μl of the MTT solutions were added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The cell survivability was analyzed by measuring
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 216 the ability of the cell’s mitochondria to reduce the yellow MTT to a purple formazan (crystals) end product. The reaction was terminated by the removal of the MTT solution. Addition of 1.0 ml of 0.04 M HCl in isopropanol to each well was used to dissolve the intracellular MTT formazan crystals. The contents of each well were mixed gently in an orbital shaker at room temperature for 1 h and the absorbency at 570 nm was measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) microplate reader (SpectraMax M5 Multi-Mode Microplate Readers Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA). Cell viability data obtained from the MTT assay were used to normalize IL-1α and IL-8 levels. CYTOKINE RELEASE MEASUREMENTS To assess the irritancy potential of aluminum-containing solutions and formulations, in vitro experiments were conducted using MatTek EpiDerm tissue model to measure the release of infl ammatory cytokines. In vitro skin samples were treated topically with 30 μl of solutions or products for 1 h in an incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2. Following the in- cubation, skin samples were washed with PBS and placed in culture medium, provided by MatTek Corporation, and continued to incubate for 24 h. After 24 h, cell culture media were collected for IL-1α release assay. IL-1α levels were analyzed by the ELISA assay kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). IL-8 levels were analyzed using immunoas- say multiplex kit (Millipore, Billerica, MA) on a Luminex X200 (Luminex Corporation, Austin, TX). PERCUTANEOUS ABSORPTION OF TAURINE Percutaneous permeation of taurine was evaluated in vitro by using human keratinocyte skin model, EpiDerm 200-X. A standard permeation device, MatTek Permeation Device was used to approximate the permeability of taurine through the skin. 5% taurine solution with or without 5% aloe extract (w/w) was applied topically to EpiDerm tissue. After set time points the EpiDerm tissue, donor and receiver solutions were collected and ana- lyzed for taurine concentration. Receiver solution was 5.0 ml PBS solution and stored at -20°C. DETERMINATION OF CELLULAR TAURINE CONCENTRATION High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine cellular taurine concentration after treating MatTek EpiDerm tissue with a 5% (w/w) taurine solution or 5% (w/w) taurine and aloe extract solution. Before analysis, tissue samples were lysed using an ultrasonic tissue lyser, Qiagen Retsch MM300 (Retsch Inc, Newtown, PA) in 500 μl of 5× Extraction Buffer (Enzo Life Sciences Inc., Farmingdale, NY). Tissue lysates were pooled together from the same treatment groups (n = 2) to ensure the adequate vol- ume needed to perform the taurine analysis. Taurine does not absorb UV/Vis radiation adequately thus, a pre-column derivatization reaction is necessary to allow for detection by HPLC. 4-fl uoro-7-nitrobenzofurazan (NBD-F) was used as a fl uorescent reagent to produce derivatives of primary and secondary amines. NBD-taurine derivative has a
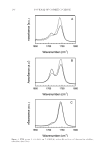
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)