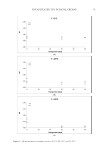
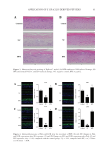
92 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE CLINICAL EVALUATION A double-blind trial was performed to evaluate BPE’s clinical effects on the allergic inflammation. Forearms of 16 adults were provoked with 10 mg/mL of histamine dihydrochloride, which simulated symptoms of allergic dermatitis. As shown in Table I, the decrease in average a* values reached 8.66 after BPE treatment, while the control Figure 5. Analysis of TSLP level by ELISA. DXMS: dexamethasone ##p 0.01, compared with the control group *p 0.05, compared with NC, n =3. Values are the mean ± SEM. Table I Changes in Erythema (a* Value) After BPE Treatment Compared With Control Groups (Double Distilled Water)a,b Double distilled water BPE Treatment Time 0 min 10 min 30 min 60 min 0 min 10 min 30 min 60 min Maximum 39.22 42.37 39.6 40.87 42.51 47.27 42.3 42.34 Minimum 17 16.16 17.12 15.53 17.42 17.92 17.75 17.65 Average 30.95 29.66 26.5 23.84 32.42 30.3 26.2* 23.76* Standard Deviation 7.79 7.82 7.12 6.69 7.68 7.16 6.5 6.01 Δa* Value – −1.29 −4.45 −7.11 – −2.11 −6.22 −8.66 a n =16. b *p 0.05. Table II Changes in Itch Intensity After BPE Treatmenta,b, Compared With Control Groups (Double Distilled Water) Double distilled water BPE Treatment time 0 min 10 min 30 min 60 min 0 min 10 min 30 min 60 min Maximum 4 4 3.5 3 4 4 3.8 3 Minimum 3 2 1 0 2.5 2 0.5 0 Average 3.7 3.23 2.36 0.97 3.51 2.86 1.73 0.53 Standard Deviation 0.43 0.84 0.9 0.89 0.56 0.78 0.9 0.88 Δ Value – −0.47 −1.34 −2.73 – −0.65 −1.78 −2.99 a n =16, data were collected from population survey based on the double-blind trial. b *p 0.05.
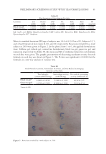
93 APPLICATION OF E GRACILIS-DERIVED PEPTIDES group was only 7.68. Although the data were not statistically significant between the BPE treatment and control group, a population survey showed that the BPE treatment significantly reduced itch intensity (Table II). According to Figure 6, a significant decrease of erythema was observed after 30 min of BPE treatment. Therefore, the clinical trials further verified that BPE treatment reduced the allergic inflammatory responses. CONCLUSION In this study, bioactive peptides were derived from E gracilis proteins. To verify their therapeutic effects on allergic inflammation, simulative experiments in 2D and 3D skin models as well as clinical trials were performed. It suggested that BPE possessed antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. It remarkably reduced the symptom development in the allergic inflammation. Therefore, the special properties guaranteed BPE as a novel cosmetic ingredient to prevent allergic skin inflammation. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31770849) and the Foundation from AGECODE R&D CENTER, Yangtze Delta Region Institute of Tsinghua University, Zhejiang (No. 2020330401000436). REFERENCES (1) F. Apone, A. Barbulova, and M. G. Colucci, Plant and microalgae derived peptides are advantageously employed as bioactive compounds in cosmetics, Front. Plant Sci., 10, 756 (2019). (2) A. Sánchez and A. Vázquez, Bioactive peptides: A review, Food Qual. Saf., 1, 29–46 (2017). (3) C. A. Ovando, J. C. Carvalho, G. Vinícius de Melo Pereira, P. Jacques, V. T. Soccol, and C. R. Soccol, Functional properties and health benefits of bioactive peptides derived from Spirulina: A review, Food Rev. Int., 34, 34–51 (2018). (4) B. Zakryś, R. Milanowski, and A. Karnkowska, Evolutionary origin of Euglena, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 979, 3–17 (2017). Figure 6. Illustrative examples of BPE’s clinical effect on histamine-induced dermatitis based on the double- blind trial from a 52–year-old woman. (A) Double-distilled water treatment (B) BPE treatment.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)