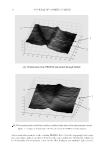
EVALUATION ON AN OPTICAL SCANNING DEVICE 17 Figure 8. Rendered ima ges of skin in vivo from the data captured from the Skin Analyzer and PRIMOS devices. either normal or critical skin surfaces can be correctly recovered. Even though the PRIMOS has been considered as a fi eld standard for skin data recovery, in some cases, lack of credibility due to the basic recovery principle employed is observed. REFERENCES (1) A. O. Barel, M. Paye, and H. I. Maibach, Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology, 4th Ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2014). (2) L. Tchvialeva, H. Zeng, I. Markhvida, D.I. McLean, H. Lui, and T. Lee, Skin Roughness Assessment, New Developments in Biomedical Engineering, D. Campolo. Ed. (InTech, 2010), pp. 341–358. (3) T. W. Fischer, W. Wigger-Alberti, and P. Elsner, Direct and non-direct measurement techniques for analysis of skin surface topography. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol., 12(1–2):1–11 (1999). (4) J. Y. Han, G. W. Nam, H. K. Lee, M. J. Kim, and E. J. Kim, New analysis methods for skin fi ne- structure via optical image and development of 3D skin Cycloscan™. Skin Res. Technol., 21, 387–391 (2015). (5) B. G. Rosén, L Blunt, and T. R. Thomas, On in-vivo skin topography metrology and replication tech- niques, J. Phys. Conf. Ser., 13, 325–329 (2005). (6) T. S omthong and Q. Yang, Surface roughness measurement using photometric stereo method with coordinate measuring machine. IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Taipei, pp. 1–6 (2016). (7) J. S un, Z. Liu, Y. Ding, and M. Smith, “Recovering skin refl ectance and geometry for diagnosis of melanoma,” in Computer Vision Techniques for the Diagnosis of Skin Cancer, S. Jacob and C. M. Emre. Eds. (Springer, Germany, 2014), pp. 243–266. (8) Z. L iu, J. Sun, M. Smith, and L. Smith, Incorporating clinical metadata with digital image features for automated identifi cation of cutaneous melanoma. Br. J. Dermatol., 169(5):1034–1040 (2013). (9) Z. L iu, Innovative lesion modeling for computer-assisted diagnosis of melanoma, PhD thesis, (Univer- sity of the West of England, 2012). (10) R. J. Woodham, Refl ectance Map [M]//Computer Vision. (Springer, New York, 2014), pp. 671–674. (11) S. Tozza, R. Mecca, M. Duocastella, and A. Del Bue, Direct differential photometric stereo shape recov- ery of diffuse and specular surfaces. J. Math. Imaging Vis., 56(1):57–76 (2016). (12) W. Smith and F. Fang, Height from photometric ratio with model-based light source selection. Comput. Vis. Image Und., 145, 128–138 (2016).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)