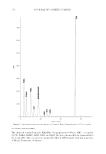
SPF TESTING METHODOLOGIES 191 methodologies. There seems to be no clinically signifi cant difference or statistically sig- nifi cant difference between the average SPF of P2 generated by different methodologies (Table IV), when examined by two different approaches. This suggests that slightly alter- native methodologies may result in similar SPF values. The SPF label value will differ between ISO 24444 and 2011 FDA-Final Rule because the 2011 FDA-Final Rule methodology, unlike the ISO 24444 methodology, subtracts the “A” value from the average SPF. The SPF label value then becomes the next lower integer after subtraction (6). The A value is the product of the upper 5% point of the t-distribution and the standard deviation, divided by (n), where n equals the number of subjects with valid data (minimum 10). This subtraction reduces the label SPF value to an integer that would, except under unusual circumstances, be different from the SPF value determined by ISO 24444, resulting in identical formulations labeled with differ- ent SPF values. AGE AND GENDER OF SUBJECT ANOVA revealed no statistically signifi cant effect of age (p = 0.126) or gender (p = 0.657) on the SPF of P2. As a result, it cannot be ruled out that any effects on the SPF of P2 are likely due to chance alone. This lack of age effect on the SPF of P2 fails to support the age restrictions placed on subjects by 2011 FDA-Final Rule and by ISO 24444. TYPE OF SOLAR SIMULATOR There are two basic types of solar simulators (Solar Light Company) used in SPF testing (12), single-port solar simulators (150 and 300 W) and multiport solar simulators (150 and 300 W). ANOVA of the data for 291 observations evaluated following use of single- port solar simulators versus 2,212 observations evaluated following use of multiport solar simulators indicated no statistically signifi cant differences (p = 0.373) in the SPF of P2. This is consistent with reciprocity holding for the wattage (13,14) and for the type of solar simulator. The type of solar simulator (Tables II and III) seems to have no signifi cant effect on the SPF of P2 (13,14). FITZPATRICK SKIN PHOTOTYPE Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype was created to assist in the prediction of MED for photo- therapy in a physician’s offi ce (15,16). Phototype was determined using either a subjec- tive assessment based on the patient’s phenotype (hair color, eye color, etc.) (15) and later on the subject’s recollection of his burning and tanning response to sun exposure (16). Because these two different subjective methods were proposed to determine Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype, confl icting Fitzpatrick Skin Phototypes can be generated for the same person. Despite its inability to predict MED (21) and increasing limited relevance (22), Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype use has been expanded over the past 40 + years. Recently, however, Individual Typology Angle (ITA) (23) has been found to be a better predictor of MED and is included in ISO 24444 as an alternative to Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype for subject qualifi cation.
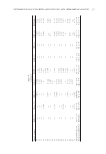
Table IV Comparison of SPF Testing Parameters ISO 24444 versus 2011 FDA-Final Rule Parameters ISO 24444 2011 FDA-Final Rule Source of UVR % RCEE defi ned in different bands λ range (nm) RCEE (%) λ range (nm) Erythemal effective radiation (%) Acceptance limits %RCEE UVAII/ UVAI ≤290 0.1% ≤290 0.1% 290–300 1.0–8.0 290–300 1.0–8.0 290–310 49.0–65.0 290–310 49.0–65.0 290–320 85.0–90.0– 290–320 85.0–90.0 290–330 91.5–95.5 290–330 91.5–95.5 290–340 94.0–97.0 290–340 94.0–97.0 290–400 99.9–100 290–400 99.9–100 UVAII 20% UVAI 60% of the total UV irradiance to ensure that appropriate amounts of UVA radiation are included UVAII 20% UVAI 60% of the total UV irradiance to ensure that appropriate amounts of UVA radiation are included Sunscreen application Amount 2.00 ± 0.05 mg/cm2 2 mg/cm2 Preparation Test area may be cleaned with a dry cotton pad or equivalent None Conditions 22 ± 4C None Application Finger cot is optional Finger cot required Spreading time 35 ± 15 s None Dry time 15–30 min ≥15 min JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 192
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)