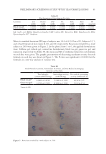
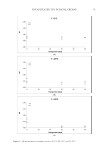
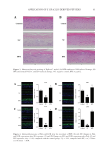
Table I Modes of Action and Maximum Concentrations Allowed for Antimicrobial Preservatives Substance CAS number Mode of action Maximum concentration allowed a Other Reference Benzalkonium chloride (BAC) 8001-54-5 • Decreases surface tension • Inactivates enzymes • Degrades cell-proteins 0.1% Avoid contact with eyes (16–18) Benzoic acid (BEC) Sodium benzoate (SB) 65-85-0 532-32-1 • Acidifies the external environment, making it unfavorable to microbial growth • Inhibits enzymes from the cellular metabolism 2.5% (acid) – rinse-off products, except oral care 1.7% (acid) – oral care 0.5% (acid) – leave-on products (19,20) Benzyl alcohol (BA) 100-51-6 • Induces membrane lysis in bacteria • Denatures the structure of proteins by binding to amino acid residues 1% (12,21) Caprylyl glycol (CG) 1117-86-8 • Destabilizes and disrupts the microbial cell membrane and may inhibit DNA synthesis 0.5–1% Up to 5% (22,23) Chloroxylenol (CX) 88-04-0/ 1321-23-9 • Causes membrane damage, resulting in leakage of cytoplasmic constituents 0.5% (18,24) Chlorphenesin (CP) 104-29-0 • Denatures proteins • Inhibits protein synthesis 0.3% (12,25) Ethylhexylglycerin (EEG) 70445-33-9 • Disrupts membrane integrity • Affects the interfacial tension at the cell membranes of microorganisms 0.5–2% Up to 2% -sprayed products Up to 8% -maximum in rinse-off products (4,26–28) 99 PRESERVATION OF PERSONAL CARE AND COSMETIC PRODUCTS
Methylparaben (MP) Ethylparaben 99-76-6 120-47-8 • Acts by disrupting membrane transport processes • Inhibits protein synthesis (ATPases/ phosphotransferases) • Inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis • Causes leakage of cytoplasmic contents • Inhibits oxygen consumption of mitochondria in fungi 0.4% (acid) for a single ester 0.8% (acid) for a mixture of esters (12,17,29) Propylparaben (PP) Butylparaben 94-13-3 94-26-8 0.14% (acid) for the sum of the individual concentrations 0.8% (acid) for a mixture of methyl and ethylparaben, but not exceeding 0.14% Not to be used in leave-on products designed for application on the diaper area of children under three years of age Natural antimicrobial agents • Denatures membrane proteins • Inactivates enzymes • Destabilizes the proton motive force and electron flow • Mediates active transport and coagulation of the cell content • Causes breakdown of the permeability barrier • Inhibits the synthesis of DNA, RNA, proteins, and polysaccharides • Effects metabolic pathways and cell division (4,30–38) Phenoxyethanol (PE) 122-99-6 • Causes membrane damage, resulting in leakage of cytoplasmic constituents • Prevents cell growth by inhibiting DNA and RNA biosynthesis • Acts on energy metabolism through inhibition of malate dehydrogenase • Disrupts the proton gradient 1% Intended for leave-on products designed for application on the diaper area of children under three years of age (28,39– 43) Sorbic acid (SA) Potassium sorbate 110-44-1 246-376-1 • Acidifies the cytoplasm by the penetration of uncharged organic acids • Changes the fluidity of the plasma membrane 0.6% (acid) (44,45) a Maximum concentration according to Annex V of Regulation European Commission No. 1223/2009 or usual concentration for unregulated. 100 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)