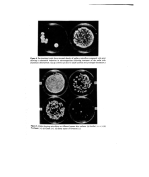
22 H. Dixon and A. K. Panezai medium). The velvet head of the sampler is pressed firmly into the axilla, and then applied to the same area of culture plate. After suitable incubation a microbial print of the axilla surface is obtained. Brain Heart Infusion Agar (B.H.I.A.) supplemented with 0.55/o Tween 80 is recom- mended for the isolation of axillary bacteria. After 24-48 h, the common resident bac- teria, staphylococci, pigmented micrococci and diphtheroids may be readily seen and identified. TESTING A DEODORANT FOR ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY IN VITRO For this purpose a modified agar diffusion test is used. The method of evaluation departs from standard procedure by using freshly isolated resident axillary micro flora as test organisms in place of type culture or stock culture strains which have been passaged several times artificially. For economy, the test is carried out by using small disposable Petri dishes 60 x 13 mm (Sterilin). About 12 ml of B.H.I.A. are poured into each dish. When hardened the agar is inoculated by means of the axilla sampler as previously described. A 6-mm antibiotic assay disc (Whatman) is impregnated with the test deodorant and placed in the centre of the print. Blank discs impregnated with sterile water and a reference standard consisting of the test antimicrobial in simple aqueous solution should be set up at the same time. Dishes are incubated at 37øC for 24 to 48 h after which zones of inhibition are recorded (Fig. 2). INTERPRETATION A deodorant with good antibacterial potential should give a well-defined clear zone of inhibition. Antimicrobial activity is sometimes modified by interaction with other formu- lation ingredients. Such interaction can be dramatically revealed by comparing the activity of th• antimicrobial in aqueous solution with the finished product containing the same active ingredient (Fig. 3). For products which may exhibit antibacterial activity but diffuse poorly, the following direct contact method is recommended. DIRECT CONTACT IN VITRO TEST A sterile filter circle (Whatman 4.25 cm) is treated with test material, drained, and applied to an axilla print for 1 h after which it is removed. Suitable controls should be prepared at the same time consisting of sterile filter circles treated with sterile water, the appropriate solvent and the product without active ingredient. Circles are removed after 1 h as in the test procedure. Plates are incubated at 37øC and presence or absence of growth recorded after 24 and 48 h. EVALUATION OF PRODUCT'S ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY IN VIVO Skin lipids are known to have the effect of greatly reducing the activity of some antimicro- bial agents, so that for realistic results the product needs to be evaluated on the skin, and for deodorants, the axilla is the appropriate area for testing. Before commencing the trial it is important to establish that toiletries which contain antimicrobial agents (anti-
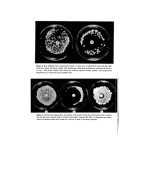
Figure 1. Velvet Pad Axi!lary Skin Sampler. Facing p. 22
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)