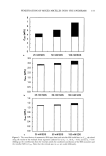
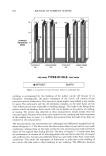
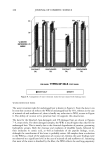
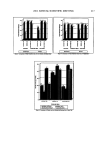
VITAMIN E ACETATE PENETRATION STUDIES 129 -- 20 •=•=•=•=•=z•=•=•z-•=•=•=•=•=•-------•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•===•==•==•==•=•=•==•=•=•-- o stri::i!.:'i•?.--"'..'":l::iiii'"'"•"•:•'":• :--... ' '"'"'"'•'"•"'""'"'"•:'•':•::•:••••!•i •ii•:•jjj•i•:•ii:i!•i•`•`•:••••i•:• '"'"' ":4•'.."4:ii•iii•':'"::•3.....'".'.'•i• i•i?•:•j•ii•:•:•:•:•i•i•:•:•:•: ::•:•i•:i•::• ::•"::'v'•:..•. Tapes containing fractional vitamin E acetate contributing to total SO-penetrated amount • Results by UV-Spectroscopy • HPLC-results Figure 6. Results (lag/cm 2) of vitamin E acetate determination by spectroscopy and the HPLC method after adhesive tape application. Amounts from LC, RP, and RS formulations found in various strips after exposure periods of 0.5 h (A) and 1.5 h (B), respectively. results of both methods are quite comparable. The result of the first tape may be artefactual due to the entrapped material that was not completely removable. For the HPLC method the whole strip was used, whereas for the spectroscopic assay only strip locations were evaluated. However, for both methods a higher accuracy can be achieved by quantifying the individual number of corneocytes sticking to the tape. The BUS-irritation assay differentiates biochemically between activation/reversible in- jury or death of epidermal cells using whole skin biopsies. Therefore, rubbing or strip- ping the skin induces a reversible activation of epidermal cells, e.g., an increase of the arachidonic acid metabolism, but no cytotoxic action to keratinozytes at all (unpublished results). There are also anatomical differences between irritancy (reversible injury) and cytotoxicity. In reconstructed human skin equivalents (RE-DED cultures) it was shown that the MTT-positive cells could be attributed to the lower cell layers, whereas the terminally differentiated keratinozytes may not be involved (12). In this irritation study with three cream formulations, no difference was observed for the cytotoxic activity, which usually occurs in the basal and suprabasal epidermal cells. Neither type of for- mulation was able to alter the activity of the basic cream under exposure conditions of 60 minutes from the beginning. The results only indicate biological activity regarding the arachidonic acid metabolism that was more active by using Rovisome © as liposomal carrier than by using microparticles or the liposome-free cream. This indicates activation but no irritation of the upper epidermal cells that may contribute to the high uptake of vitamin E acetate into the horny layer under short-term exposure. Vitamin E acetate in Rovisome © as liposomal carrier delivered most of the bioactive substance into the skin, compared to other formulations such as the lameliar cream (LC) or a microparticle-based one (Roviparts©). The reasons for the difference can be explained
130 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE by an alteration of the plasticity of the horny layer, inducing a strong reservoir capacity and activation of epidermal cells. Additionally, an opening of the potential pathway for a follicular penetration may be part of an increased reservoir capacity (13). According to a hypothetical example, Schaefer and Redelmeier (3) illustrated that dif- fusion through the "shunt" pathway may be relatively more important at an early stage, within a first period of approximately 90 minutes. At a later time, the flux through the stratum corneum is generally more important. Formulations using Rovisome © vesicles may take advantage of both the "shunt" pathway immediately after the application and the conventional pathway during the extended exposure time. CONCLUSIONS For the quantitative spectrometric assay, a classical least-squares evaluation of the spectra between 265 nm and 350 nm based on the constituent spectra was used. It can be concluded that the spectral measurement is extremely fast, and a calibration can be based on a few reference spectra only. Therefore, UV/VIS spectroscopy is an economic ana- lytical method for evaluating large numbers of samples of the horny layer taken by the adhesive tape stripping method. The latter is an established tool for the depth profiling of substances within the stratum corneum. Regarding the irritation test, no cytotoxicity was recorded for the three formulations. However, Roviparts ©- and Rovisome©-formulated creams induced a considerable acti- vation of the upper epidermal cells, possibly contributing to the penetration efficiency of Rovisome©-formulated vitamin E acetate by increasing the reservoir capacity. Rovi- some©-formulated creams were most successful in vitamin E acetate delivery into the horny layer, which can be explained by an alteration in the corneal plasticity and by opening the additional pathway for a follicular penetration. REFERENCES (1) Th. F6rster, W. Pittermann, M. Schmitt, and M. Kietzmann, Skin penetration properties of cosmetic formulations using a perfused bovine udder model, J. Cosmet. Sci., 50, 147-157 (1999). (2) Th. F6rster, B. Jackwerth, W. Pittermann, W. van Rybinski, and M. Schmitt, Properties of emulsions: Structure and skin penetration, Cosmet. Toilerr. 112, 73-82 (1997). (3) H. Schaefer and Th. Redelmeier, "Factors Effecting Percutaneous Absorption," in Ski, Barrier-- Principles of Percutaneous Absorption (Karger, Basel, 1996). (4) G. Blume, W. Pittermann, M. Waldmann-Laue, M. Kietzmann, D. Verma, and C. Johann, "Rovi- some--A Carrier System for Vitamins," in Euro-Cosmetics, 3-2000 (2000), pp. 30-32. (5) L. Cordech, M. Oliva, M. Pons, A. de la Maza, A.M. Manich, andJ. L. Parra, Percutaneous penetration of liposomes using tape stripping technique, Int. J. Pharm., 139, 197-203 (1996). (6) M. Kietzmann, W. L6scher, D. Arens, P. MaaB, and D. Lubach, The isolated perfused bovine udder as an in vitro model of percutaneous drug absorption: Skin viability and percutaneous absorption of dexamethasone, benzoyl peroxide and etofenamate,J. Pharm. Toxicol. Meth., 30, 75-84 (1993). (7) K .R. Beebe, R. J. Pell, and M. B. Seasholtz, Chemometrics: A Practical Guide (Wiley, New York, 1998). (8) L. Kiipper, H. M. Heise, W. Pittermann, and L. N. Butvina, New tool for epidermal and cosmetic formulation studies by attenuated total reflection spectroscopy using a flexible mid-infrared fiber probe, Fresenius J. Anal Chem., 365,753-757 (2001). (9) W. Pittermann, B. Jackwerth, and M. Schmitt, The isolated perfused bovine udder skin model: A new in vitro model for the assessment of skin penetration and irritation, In Vitro Toxicol., 10, 17-21 (1997).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)