APPLICATION OF PURPALD® FOR DETERMINATION OF CARBOXALDEHYDES 393 solutions were diluted to produce working solutions at a concentration of 0.01 mol·l−1. APPARATUS A double-beam ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (Cary 100 Bio-Varian, Palo Alto, CA) with spectral bandwidth 0.2–4.0 nm programmable at 0.1 nm was used in the stud- ies. Spectrophotometric 10-mm quartz cells with Tefl on lids were used. In all measure- ments, the spectral bandwidth was 1.5 nm. GENERAL PROCEDURE Suitable volume of working solution of 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde and hydroxyiso- hexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde was transferred into a 10-ml in-volume fl ask and 5-ml in-volume fl ask, respectively (Table I). Then 1 ml of Purpald® solution and 1 ml of 1 mol·l−1 sodium hydroxide solution were added. The mixture was left at room tempera- ture for 45 min and then diluted to the mark with ethanol. The solutions were transferred into a spectroscopic cell and the absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 538 nm, against blank solution. The blank test was composed of 1 ml Purpald® solution and 1 ml of 1 mol·l−1 sodium hydroxide solution. The absorbance of aldehydes was referred to the standard curves of aldehydes in drug-free samples to determine concentrations. Linearity was established on the basis of the equa- tion A = aC + b where A (AUS) is the absorbance and C (mol·l−1) is the concentration of an aldehyde in a sample. The evaluation of the linearity was performed with the use of linear regression analysis. PRECISION AND ACCURACY The precision determination was conducted through the analysis of six sample solutions of 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde on the same day for intraday precision (repeatability). Table I The Results of Compounds Determination n = 6 Compound Taken (mol·l−1) Found s x t0,95. n ± (mol·l−1) RSD (%) Recovery (%) 3-Cyclohexene carboxaldehyde 2.5 × 10−5 (2.8 ± 0.1) × 10−5 2.75 110.8 5.0 × 10−5 (4.8 ± 0.1) × 10−5 2.01 96.0 1.0 × 10−4 (9.6 ± 0.3) × 10−5 3.24 96.0 2.0 × 10−4 (2.02 ± 0.04) × 10−4 2.01 101.0 3.0 × 10−4 (3.0 ± 0.1) × 10−4 3.39 100.0 Hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde 2.0 × 10−5 (1.91 ± 0.03) × 10−5 1.56 95.5 5.0 × 10−5 (4.9 ± 0.1) × 10−5 2.28 98.0 1.0 × 10−4 (1.03 ± 0.02) × 10−4 1.47 103.0 1.5 × 10−4 (1.50 ± 0.03) × 10−4 2.13 100.0 2.0 × 10−4 (2.01 ± 0.06) × 10−4 2.73 100.5
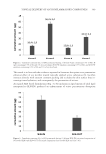
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 394 For the purpose of accuracy, the known amounts of 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde were added to sample solution (recovery test). The procedure of the test comprised the analysis of three different lotion solutions, in four replicates each, which spiked with 0.5, 1.5, and 2.5 μmol and represented the low, me- dium, and high concentrations of the linearity concentration range, respectively. STABILITY OF THE COLOR COMPOUND The preparation of stability test for 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde–Purpald® adduct was conducted. The sample was prepared according to general procedure with spiking of the sample with an appropriate amount of the aldehyde to obtain a solution of 4 × 10−4 mol·l−1 concentration. Afterward, the measurement of the absorbance was executed at room temperature for 90 min. ASSAY HYDROXYISOHEXYL 3-CYCLOHEXENE CARBOXALDEHYDE IN A DOSAGE FORM The procedure for determination of hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde in cosmetic is the same as that described for calibration procedure for 3-cyclohexene-1- carboxaldehyde. One milliliter of lotion was transferred in a test tube, then 1 ml of 0.1 mol·l−1 Purpald® solution and 1 ml of 1 mol·l−1 sodium hydroxide solutions were added. The mixture was left at room temperature for 45 min and then ethanol was added to a volume of 5 ml. Absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 538 nm, against blank test. The blank test was composed of 1 ml lotion and 1 ml of 1 mol·l−1 sodium hydroxide solution. The mixture was also left at room temperature for 45 min and then ethanol was added to a volume of 5 ml. The amount of hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde in lotion was calculated using the regression equation. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In this work, we used the reaction of aldehydes with Purpald®, which is a specifi c reagent for aldehydic group as shown in Figure 2. As a result of reaction of aldehydes with described derivatization reagent purple derivatives are formed. This reaction was taken as a base to develop a spectrophotometric method for determination of cyclohexene-1- carboxaldehyde and hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde. Figure 2. Reaction scheme between Purpald® and carbonyl compounds.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)