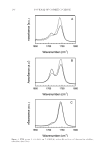
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 224 anti-irritating agents into dermatological vehicles has become necessary to mitigate the contact irritant dermatitis that arises from the usage of antiperspirants containing AlCl3. Our results have revealed the existence of a boost in anti-irritating effects that the taurine and aloe extract blend demonstrate on topical application. We observed that co-treatment with taurine and aloe extract in a PBS solution results in further inhibition of IL-1α pro- duction compared with treatments with only taurine or aloe extract in human epidermis model. EpiDerm tissue treated with 0.1% taurine and 0.1% aloe extract released lower levels of IL-1α compared with tissue treated with only 0.2% taurine or 0.2% aloe extract (Figure 4). IL-1α is a primary cytokine that is constitutively expressed by keratinocytes and plays a major role in the onset of infl ammatory responses in the skin (20). IL-1α re- lease from human epidermal equivalents is commonly measured to predict the irritation potential of consumer products and provides reliable in vivo correlation (21). We next addressed whether the anti-irritating effects of taurine and aloe extract would still be observable in oil in water emulsion formulation containing 12% AlCl3. Our Figure 6. IL-8 concentr ations in EpiDerm cell culture media (n = 3) after topical application of AlCl3 prod- ucts for 1 h. Negative control (NC) was untreated tissue and positive control (PC) was tissue treated with 12% AlCl3 solution without taurine or aloe extract. A commercial 12% AlCl3 antiperspirant product was used as a benchmark product to assess irritancy potential. Prototype 12% AlCl3 product with and without 0.1% taurine and 0.1% aloe extract actives were tested.
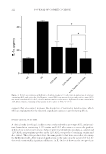
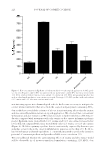
TAURINE/ALOE VERA FOR BOOSTING ANTI-SKIN IRRITATION EFFECTS 225 prototype antiperspirant product containing 0.1% taurine and 0.1% aloe extract was found to signifi cantly reduce the production of IL-1α and IL-8 compared with con- trols in EpiDerm tissue (Figures 5 and 6). IL-8 is a chemokine that exerts chemotactic effects on neutrophils and lymphocytes. Increased expression of IL-8 by keratinocytes is a non-specifi c response to tissue damage due to chemical or physical agents (22). A human clinical study was conducted to assess the irritancy potential of our prototype product, and the results demonstrated that our prototype product signifi cantly reduced the pro- duction of IL-1α compared with a benchmark product (Figure 8). A commercial 12% AlCl3 antiperspirant product was used as a control and benchmark for our irritation ex- periments. These results demonstrated the applicability of taurine and aloe extract in reducing skin irritation to dermatological vehicles. Data obtained from SEC revealed that the additional of taurine and aloe extract into formulation did not alter the size distribu- tion of Al3+. This suggests these anti-irritating agents do not affect the polymerization of AlCl3, which suggests the sweat reduction effi cacy would remain intact (Figure 1). From our studies, we were able to develop an effi cacious, antiperspirant formulation with re- duced irritation potential. Finally, we sought to understand the mechanism of the boosted anti-irritating effect of the taurine and aloe extract blend. Taurine has two largely separated pKa, a very low pK1 (1.5) from the sulfonic acid group and a high pK2 (9.08) from the amino group which give rise to a zwitterion over a wide pH range. Under our experimental pH range Figure 7. EpiDerm tissue was lysed at set time points and intracellular taurine concentration was measured using HPLC. Tissues were treated with either PBS solution containing only taurine or PBS solution with both taurine and aloe extract to assess the permeation enhancing effects of aloe extract on keratinocytes.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)