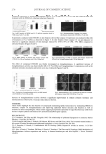
ANTI-TYROSINASE ACTIVITY OF ETHANOL FROM GRAPES 229 THE EFFECT OF PHENOLIC COMPOUNDS We suspected that phenolic compounds played important roles in anti-tyrosinase activity. Thus, the total phenolic content in the ethanol extracts from Kyoho grapes and Red Globe grapes was determined and presented as the amount of gallic acid equivalent. The total phenolic content in KG-SEE and RGG-SEE was 400±11 and 339±7 mg gallic acid equivalent/g, respectively, while KG-PEE and RGG-PEE showed 18±1 and 27±0 mg Figure 2. Michaelis-Menton equation of V versus [ S ] with KG-SEE and L-dopa. The enzymatic assay was performed with mushroom tyrosinase (44 units/ml) at room temperature for 10 min. Symbols: - - (0 mg/ml KG-SEE) - - (0.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -▲- (1.67 mg/ml KG-SEE) -×- (3.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -∗- (5 mg/ml KG-SEE). Figure 3. Lineweaver-Burk plot of 1/V versus 1/[ S ] with KG-SEE and L-dopa. The enzymatic assay was reformed with mushroom tyrosinase (44 mg/ml) at room temperature for 10 min. Symbols: - - (0 mg/ml KG-SEE) - - (0.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -▲- (1.67 mg/ml KG-SEE) -×- (3.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -∗- (5 mg/ml KG-SEE).
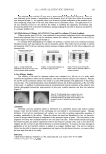
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 230 gallic acid equivalent/g (Table I). Our data indicated that the total phenolic content in ethanol extracts from grape seeds was much higher than in grape peels. The amount of phenolic compounds in the various grape derivatives parallels the anti-tyrosinase activity. Therefore, it was quite possible that phenolic compounds contributed to the anti-tyrosinase activity in the grape extracts. As the anti-tyrosinase activity in the seed extracts are the main interest, it was noted that even though KG-SEE had a higher total phenolic content than RGG-SEE, the anti- tyrosinase activity of KG-SEE was lower than that of RGG-SEE. This indicated that total phenolic content was not the only factor affecting the anti-tyrosinase activity, and that the profi le of phenolic compounds in the extracts might also be an important variable. The phenolic compounds in KG-SEE and RGG-SEE were determined by using HPLC, and the results are shown in Table II. Among the detected phenolic compounds, there were four compounds that showed a signifi cant difference between KG-SEE and RGG-SEE. RGG-SEE had higher gallic acid and kuromanin chloride content than KG-SEE, but lower catechin hydrate and ellagic acid content. After testing the anti-tyrosinase activity of these four pure phenolic compounds, we found that the anti-tyrosinase activity fol- lowed the order: gallic acid catechin hydrate kuromanin chloride ellagic acid (Figure 4). Table I Total Phenolic Content in the Ethanol Extracts from the Peels and Seeds of Kyoho Grapes and Red Globe Grapes* KG-SEE KG-PEE RGG-SEE RGG-PEE 400±11a 18±1d 339±7b 27±0c *Total phenolic content is presented as the amount of gallic acid equivalent (mg gallic acid equivalent/g). a,b,c,d The values in the same row followed by different superscripts were signifi cantly different ( p 0.05). Table II Phenolic Compounds in the Ethanol Extracts from the Seeds of Kyoho Grapes and Red Globe Grapes Determined by HPLC Compounds Content (g kg−1) KG-SEE RGG-SEE Gallic acid 2.22b 4.60a Catechin hydrate 5.49a 2.27b Kuromanin chloride — 2.75 Ellagic acid 1.61a 0.05b Flavon 0.60* 0.65 Rutin — — Chlorogenic acid — — Resveratrol — — Quercetin — — Cinnamic acid — — —Not detected. *The values in the same row are not signifi cantly different. a,b The values in the same row followed by different superscripts are signifi cantly different ( p0.05).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)