CHITOSAN PATCH INCORPORATING A. ALTILIS HEARTWOOD EXTRACT 261 performed at Cosmetics and Natural Products Research Center, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok, Thailand. Selection criteria for subjects. Healthy Thai male or female with age 20–45 year and having a melanin value, in a hyperpigmented area on facial skin, in a range of 290–490 AU were included. Subjects were excluded from the study if they had been smoking and alcoholic. Female subjects were excluded if they were pregnant or lactating. Subjects were to have discontinued topical application of any medicines, steroids, photosensitizing, or cosmetics with depigmenting agents such as tretinoin, α-hydroxy acids, β-hydroxy acids, hydro- quinone, kojic acid, and arbutin on facial skin for at least 2 weeks before study. In addi- tion, subjects were not to have used any systemic steroids, hormones, antibiotics, and antihistamines for at least 4 weeks before the study. Other exclusion criteria included subjects who had a scar or burn with a diameter of more than 2 cm per each area on face or forearm, or who had history of atopic skin reaction, eczema, psoriasis, or recurrent or active herpes simplex on face or forearm. Excessive exposure to sunlight was to be avoided. Irritation test. Subjects were screened according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. Only subjects who met the criteria entered the skin irritation test (4-h patch test), which was designed to assess the skin tolerance to the formulated patch. All subjects were asked to sign an informed consent before screening into the study. To assess the irritant contact dermatitis, the chitosan hydrogel patch incorporating the extract (the tested patch, 4 cm2 of patch containing 0.29 mg of artocarpin), 20% sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS BASF (Thai) Ltd., Bangkok, Thailand) (positive control, 0.2 ml), and distilled water (negative control, 0.2 ml) were tested using the 4-h human patch test. The testing samples were applied to the three areas on subject’s forearm. Each area was sepa- rated by 3 cm2 from each other, then covered with a Webril pad for up to 4 h. The test patch and substances were removed or wiped off from the skin. Treatment sites were as- sessed for the presence of irritation at 0.5, 24, 48, and 72 h after patch test removal. The evaluation of skin irritation was composed of objective assessment using Mexameter® (Model MX 18 Courage and Khazaka Electronic GmbH, Cologne, Germany) for skin redness measurement (erythema index) and visual assessment by a dermatologist in three domains including erythema, scaling, and oedema, according to the scale of Frosch & Kligman and COLIPA (9,12,13). Effi cacy test. The study design was a randomized, double-blind and parallel study. The site of testing was the facial skin. The subjects were randomly assigned to either receive the test patch (size of 4 cm2 of the formulated patch containing 0.29 mg of artocarpin, test group) or the control patch (size of 4 cm2 of the formulated patch without the extract, control group) applying it to the hyperpigmented area. The control patch had components simi- lar to the test patch but without the extract. To determine the balance in skin properties of the two groups, their skin properties at the hyperpigmented area were evaluated before (baseline, week 0) and after patch application. Duration of the study was 8 weeks. At week 0 of the study, subjects arrived at the testing room at 8.00 am. They were asked to wash their non–make up face with clean water, pat the face dry with a towel, and wait for 30 min before proceeding to the next procedure of measuring the skin properties. The temperature and humidity of the test room were controlled to 25 ± 2°C and 50–70% RH, respectively. Skin properties including skin colors (melanin and erythema values), moisture content and skin pH of the hyperpigmented area were measured by using Mexameter®, Corneometer® (Model CM285 Courage and Khazaka Electronic GmbH) and
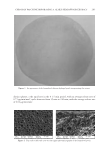
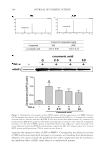
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 262 Skin-pH meter (Courage and Khazaka Electronic GmbH), respectively. After completing baseline measurements, color photographs of subjects were taken. After that, all subjects received the test or control patch (three pieces/1 week usage) for using at home and were asked to record in their diary any abnormal sensation and/or feeling from the application of the patches. Subjects were instructed to apply the received patches every two days (Monday, Wednesday, and Friday) by slightly pressing them on the hyperpigmented area at night after facial cleansing. The duration of application for each night was 30 min. Any facial product except products containing steroids, photosensitizing, and depigmenting agents were allowed to be used at the patch-applied area after 20 min of the patch ap- plication. At week 1, 3, 6, and 8 of study period, subjects arrived at the test room around 8.00 am and waited for 30 min before evaluation of their skin properties. The dermatolo- gist also assessed the irritation score on the applied area. Subjects were asked to return the package of used products while receiving the new one at each visit. In addition, the ap- plication time recorded in the personal diary was also examined. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS All data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Student’s t-test was used for comparison the skin parameters between two independent groups, and analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for multiple comparisons. p 0.05 was considered statisti- cally signifi cant. RESULTS CONTENT OF ARTOCARPIN IN THE ARTOCARPIN-ENRICHED EXTRACT The extract was a dry yellow powder. The artocarpin content was 89.5 ± 6.5% w/w, ac- cording to an HPLC assay. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE FORMULATED CHITOSAN HYDROGEL PATCH INCORPORATING THE EXTRACT When the chitosan solution was blended with the microemulsion in the ratio of 1:1 by weight, it was observed that they were compatible. The formulated patches were yellow- ish, transparent, and glossy in appearance (Figure 1). The ultimate tensile strength of the patches was 5.07 ± 0.08 N/mm2, the percentage of elongation at the break point was 35.04 ± 0.14%, and the moisture content was 51.4 ± 0.9%. The surface morphology of the formulated patches was rough and porous as can be seen in the photomicrographs (Figure 2). RELEASE OF ARTOCARPIN FROM THE FORMULATED PATCH INCORPORATING THE EXTRACT Figure 3 illustrates the cumulative amount of artocarpin released from the formulated patch after 30 min (67%) and after 240 min (86%). The release pattern exhibited two
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)