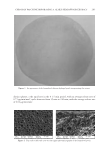
BACTERIAL CONTAMINATION OF LIPSTICK 249 Phylum Class Genus Number Lactococcus 12 Streptococcaceae_uc 24 Streptococcus 1,492 Clostridia Clostridiales_uc_g 1 Blautia 2 Lachnoanaerobaculum 1 Lachnospiraceae_uc 1 Shuttleworthia 12 Eubacterium_g11 7 Faecalibacterium 1 Ruminococcaceae_uc 3 Negativicutes Dialister 6 Selenomonas 2 Veillonella 34 Fusobacteria Fusobacteria_c Fusobacterium 13 Leptotrichia 28 Nitrospirae Nitrospira_c Nitrospira 1 Planctomycetes Planctomycetacia Planctomycetacia_uc_g 1 Planctomycetaceae_uc 2 Proteobacteria Alphaproteobacteria Caulobacter 7 Bradyrhizobium 45 Devosia_f_uc 1 Bosea 1 Methylobacteriaceae_uc 35 Methylobacterium 2,969 Rhizobiaceae_uc 1 Rhizobiales_uc_g 2 Rhizomicrobium_f_uc 1 Rhodospirillales_uc_g 3 Rickettsiaceae_uc 1 Altererythrobacter 1 Sphingomonadaceae_uc 2 Sphingomonas 36 Betaproteobacteria Rhodoferax 1 Derxia_f_uc 1 Lautropia 46 Kingella 1 Neisseria 189 Neisseriaceae_uc 3 Simonsiella 4 Dechloromonas 2 Zoogloea 1 Table I Continued
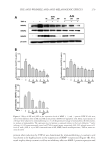
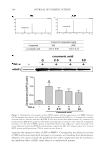
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 250 Phylum Class Genus Number Gammaproteobacteria Cardiobacterium 10 Enterobacter 7 Escherichia 13 Salmonella 2 Trabulsiella 1 Halomonas 5 Oceanospirillales_uc_g 1 Haemophilus 712 Pasteurellaceae_uc 16 Acinetobacter 5 Moraxella 27 Moraxellaceae_uc 2 Pseudomonadaceae_uc 5 Pseudomonas 190 Pseudomonadales_uc_g 1 Lysobacter 4 Xanthomonadaceae_uc 1 Xanthomonadales_uc_g 1 Saccharibacteria_TM7 Saccharimonas_c Saccharimonas 9 Verrucomicrobia Verrucomicrobiae Pedosphaera_f_uc 2 Unkown 102 Total 19,863 Table I Continued Repeated use of cosmetics can cause microbial contamination and infection (14). In general, cosmetics should be free from the following bacterial species: S. aureus, E. coli, Salmonella spp., C. albicans, Clostridium spp., and P. aeruginosa (3). Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas were identifi ed in this experiment, whereas pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia and Salmonella were found to spread through the fecal-oral route. In addition, oral bacteria associated with disease, such as Actinomyces, Porphyromonas, and Fusobacterium were found. Pathogenic bacteria such as Corynebacterium and Neisseria were also found in this study. In particular, Corynebacterium diphtheriae of the Corynebacterium genus is the cause of diphtheria (15). Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae of the Neisseria genus cluster on the mucosal surfaces of humans. The former is known to cause sepsis and meningitis, whereas the latter causes gonorrhea (16). As our sequencing was not deep enough to identify the particular species present, additional studies will be needed to determine whether these pathogenic bacteria are present in lipstick. In addition, a genus was considered pathogenic if any one of its members were known pathogens. Therefore, the actual proportion of pathogenic bacteria might be lower than reported here. Previous studies examining bacterial contamination of lipstick using classical bacterial cultures have reported contamination by various species. Onondaga et al. conducted a Gram stain and biochemical test on 20 lipstick samples (3) and observed contamination by S. aureus and C. albicans. Sawant et al. examined 12 lipstick samples for contamination before and
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)