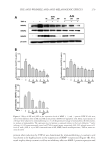
CHITOSAN PATCH INCORPORATING A. ALTILIS HEARTWOOD EXTRACT 265 or redness when compared with baseline. Based on the dermatologist’s reports and the self-reporting by the subjects, no sign of skin irritation was observed throughout the study. By interviewing the subjects and assessing their diaries, we found that all subjects followed the instructions of product application. They also avoided sun exposure by wearing protective facial covering or hat. DISCUSSION Our previous studies reported that A. altilis heartwood extract contains artocarpin as a major constituent and has a potent inhibitory activity on melanin production in B16F1 melanoma cells and UVB-induced hyperpigmented dorsal skin of brownish guinea pigs (4,5). There are three important mechanisms of the extract, variously discussed, which inhibits melanogenesis: (a) inhibition of tyrosinase activity, (b) inhibiting transportation of tyrosine, and (c) inhibiting melanin production in the melanosome (4,12). In the present study, the extract from A. altilis heartwood was isolated, formulated into o/w microemul- sion and then incorporated in the aqueous polymer, chitosan, which acted as a polymeric Figure 4. S LS-irritated skin of volunteers forearm after 4-h treatment of 20% SLS (a) and erythema values of subjects forearm treated with 20% SLS, distilled water and the tested patch for 4 h (b). Each bare rep- resents mean ± SD of erythema value in arbitrary unit (AU). (n = 59 *p 0.05 by unpaired student’s t-test).
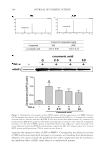
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 266 Table I Demogr aphic and baseline characteristics of subjects enrolled in the effi cacy study (N = 59) Characteristics Test group (n = 30) Control group (n = 29) p* Age, mean (SD), year 41.3 (6.9) 42.2 (6.9) 0.618 Sex, no. (%) Male 2 (6.7) 1 (3.5) Female 28 (93.3) 28 (96.5) Race, no. (%) Thai 30 (100) 29 (100) Education, no. (%) Primary school 20 (66.7) 18 (62.1) High school 10 (33.3) 8 (27.6) Bachelor’s degree or equivalent - 3 (10.3) Occupation, no (%) Agriculturalist 3 (10) 3 (10.3) Freelance/personal business 5 (16.7) 6 (20.7) Contingent worker 22 (73.3) 20 (69.0) Skin properties, mean (SD) Melanin value, AU 370.8(2.8), 369.1 (4.1) 0.812 Moisture content, AUa 45.7 (3.3) 46.9 (4.3) 0.233 Skin pH 5.6 (0.5) 5.5 (0.5) 0.446 Erythema value, AU 417.7 (3.4) 418.1 (3.4) 0.653 AU: arbitrary unit. *2-Group t-test with a 2-sided signifi cance level of 0.05. a One unit represents a water content of stratum corneum of 0.02 mg/cm2. device for delivering the bioactive compound to the skin. We observed that the bioactive components of the A. altilis heartwood extract were released from the formulated patch at the effective amount, resulting in the depigmenting effi cacy in the clinical study. Our experimental process began with the preparation of the A. altilis heartwood extract. We then analyzed the extract by using HPLC. Our analysis showed a high content of arto- carpin (89.5 ± 6.5% w/w) in the prepared extract, which coincides with the 90.6 ± 5.1% w/w of artocarpin reported in our previous study (7). These results clearly indicate that artocarpin is a major compound of the A. altilis heartwood extract. For the formulation of the chitosan hydrogel patch, lactic acid was used to dissolve chitosan (9,10,13), and the chitosan solution was then blended with the extract microemulsion by stirring. The blended solution did not show incompatibility because of the external phase of the microemulsion being water which is miscible with the aqueous solution of the polymer. The formulated patches showed proper fl exibility with tensile strength in the range of 5–10 N/mm2 and percentage elongation at break point in the range of 20–50%. These values allow the patches to be handled and to adhere to the skin (9,10,14). The fl exibility of the formulated patches is possibly caused by the plasticizer activity of the incorporated ingredients, such as lactic acid (9,10,15), NaCl (16,17), and glycerin (18,19) which together interrupt the compactness of the polymeric network. As well, the hygroscopic behavior of these plasticizers kept the patch in a hydrogel state and main- tained a high moisture content. Water remaining in the hydrogel patch supported the incorporated microemulsion surfactant (Tween® 80) by solubilizing the IPM oil which is a dissolving solvent in the extract.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)