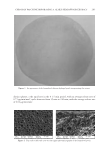
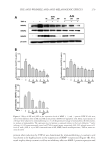
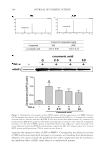
BACTERIAL CONTAMINATION OF LIPSTICK 247 two or more ambiguous nucleotides, a low-quality score (average score 25), or reads shorter than 300 bp were discarded. Potential chimerical sequences were detected using the Bellerophon method consisting of comparing the BLASTN search results between the forward and reverse half sequences (7). After removing chimerical sequences, the taxonomic classifi cation of each read was assigned against the EzTaxon-e database (http://eztaxon-e. ezbiocloud.net) (8). Briefl y, this database contains the 16S rRNA gene sequences of type strains along with valid published names and representative species phylotypes of cul- tured and uncultured entries in the GenBank database. Complete hierarchical taxonomic classifi cations from phylum to species are also included. PATHOGENIC BACTERIA ANALYSIS Cases within the last 10 year reporting the pathogenicity of each identifi ed bacterial genera identifi ed were searched for using PubMed. Pyrosequencing results were matched to the genus level, with the limitation that the analysis could not be completed up to the species level. Therefore, a genus was considered pathogenic when any one of the species belonging to it had a reported case of pathogenicity. RESULTS A total of 19,863 sequence reads were obtained and 105 genera of bacteria were identifi ed (Table I). The bacteria identifi ed included those found not only on the skin, but also in saliva and water. Leifsonia (65.86%), Methylobacterium (14.95%), Streptococcus (7.51%), and Haemophilus (3.58%) were predominant among all identifi ed genera (Figure 1). Patho- genic bacteria such as Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Salmonella, Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium, and Neisseria were also found. These potentially pathogenic bacteria represented 27.6% of the 105 genera, whereas the four most dominant genera comprised 92% of the 19,863 total reads. Actinomyces, Bacteroides, Porphyromonas, Prevotella, Capnocy- tophaga, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Veillonella, and Fusobacterium were among the oral bac- teria identifi ed. The most commonly identifi ed oral bacteria belonged to the Streptococcus genus. DISCUSSION The most commonly identifi ed bacteria overall belonged to the Leifsonia, a genus of aquatic bacteria commonly found in water. Although the particular species was not identi- fi ed, Leifsonia aquatica, a bacterium belonging to the Leifsonia genus, causes catheter- related disease and, in rare cases, acute sepsis in immunocompromised patients (9,10). The next most commonly identifi ed genus, Methylobacterium, comprises opportunistic pathogenic bacteria that cause infections in immunocompromised individuals (11). Streptococcus, the third most commonly identifi ed genus, is composed of gram-positive bacteria found in large numbers in the oral cavity and saliva, attaching to the oral mucosa and the surfaces of teeth (12). The fourth most common, Haemophilus, includes life- threatening microorganisms that cause respiratory infection and are known to have wide pathogenicity (13).
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 248 Table I List of all bacterial genera identifi ed in lipstick using pyrosequencing Phylum Class Genus Number Bacteria Acidobacteria Solibacteres Paludibaculum 1 Actinobacteria Acidimicrobiia Acidimicrobiaceae_uc 1 Actinobacteria_c Actinobacteria_c_uc_g 2 Actinomyces 42 Actinomycetaceae_uc 1 Scardovia 1 Corynebacteriaceae_uc 1 Corynebacterium 12 Mycobacterium 5 Rhodococcus 2 Calidifontibacter 15 Arsenicicoccus 4 Janibacter 2 Agromyces 1 Cnuibacter 1 Diaminobutyricibacter 2 Leifsonia 13,081 Microbacteriaceae_uc 276 Rothia 120 Micrococcales_uc_g 13 Propionibacterium 12 Coriobacteriia Atopobium 2 Rubrobacteria Gaiellaceae_uc 1 Bacteroidetes Bacteroidia Bacteroides 2 Bacteroidales_uc_g 1 Porphyromonas 8 Alloprevotella 1 Prevotella 23 Flavobacteria Capnocytophaga 4 Chryseobacterium 5 Elizabethkingia 3 Sphingobacteriia Sphingobacteriia_uc_g 1 Chlorofl exi Caldilineae Caldilineaceae_uc 1 Deinococcus-Thermus Deinococci Deinococcus 3 Thermus 4 Firmicutes Bacilli Paenibacillaceae_uc 1 Staphylococcaceae_uc 2 Staphylococcus 59 Gemella 16 Granulicatella 7 Lactobacillus 9 Lactobacillales_uc_g 1 Leuconostoc 2
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)