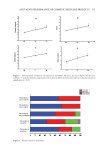
588 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE pro-FLG, which is proteolytically cleaved and converted to FLG (35). FLG is a filament- associated protein that plays an essential role in maintaining epidermal homeostasis (e.g., epidermal hydration and skin barrier function) (36,37). FLG deficiency is highly associated with TEWL, dryness, and bacterial colonization, which confers susceptibility to itch (38– 41). Besides inherited loss-of-function mutations, several inflammatory cytokines, including IL4 and IL13, can induce the suppression of FLG expression at the transcriptional level in AD (20,42,43). Therefore, it has been suggested that restoration of reduced FLG expression by inflammatory cytokines may help relieve itchy skin. Here, we confirmed that treatment with IL4 + IL13 downregulated FLG mRNA expression in a time-dependent manner, as revealed by RT-PCR (Figure 3A) and qPCR (Figure 3B). IL4 + IL13 decreased FLG mRNA levels by 0.98 ± 0.015-, 0.87 ± 0.045-, 0.71 ± 0.036-, and 0.48 ± 0.076-fold increases at 6, 12, 24, and 36 h, respectively, of the control. Consistent with mRNA levels, a time-dependent decrease in pro-FLG protein levels by IL4 + IL13 stimulation was observed using immunoblot analysis (Figure 3C). To Figure 3. Effect of the three herbal extracts on the restoration of IL4 + IL13-induced suppression of FLG expression in HaCaT cells. (A and B) HaCaT cells were treated with IL4 (20 ng/mL) plus IL13 (50 ng/mL) for various time periods (0–24 h). Total RNA was isolated, and FLG mRNA levels were examined using RT-PCR (A) and qPCR (B). GAPDH was used as the loading control. (C) HaCaT cells were treated as in (A), and whole- cell lysates were immunoblotted using anti-FLG antibodies. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (D and E) HaCaT cells were treated with IL4 (20 ng/mL) plus IL13 (50 ng/mL) for 36 h in the absence or presence of A houstonianum (40 μg/mL), B falcatum (20 μg/mL), S chinensis (40 μg/mL), or a combination of the three. Total RNA was isolated, and FLG mRNA levels were examined using RT-PCR (D) and qPCR (E). GAPDH was used as the loading control. (F) HaCaT cells were treated as in (D), and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using anti-FLG antibodies. GAPDH was used as the loading control. Relative band intensities were measured using ImageJ. ns: not significant *p 0.05, **p 0.01, ***p 0.001 compared to control (n = 3).
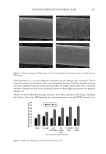
589 SUPPRESSION OF ITCHING BY THREE HERBAL ETHANOLIC EXTRACTS investigate whether the three medicinal herbs affect FLG mRNA expression, we treated HaCaT cells with IL4 + IL13 in the presence or absence of A houstonianum, B falcatum, S chinensis, and a combination of the three. We found that the downregulation of FLG mRNA expression induced by IL4 + IL13 was significantly (p 0.01) restored by single or combination treatment, as revealed by RT-PCR (Figure 3D) and qPCR (Figure 3E). The decrease in the abundance of pro-FLG protein by IL4 + IL13 stimulation was significantly (p 0.001) restored in the presence of A houstonianum, B falcatum, S chinensis, and a combination of the three (Figure 3F). Double immunofluorescence staining showed that IL4 + IL13 stimulation decreased the punctate patterns of FLG protein staining (Figure 4). However, pretreatment with a combination of the three extracts restored punctate staining similar to that of the control cells. These data suggest that A houstonianum, B falcatum, and S chinensis alone or in combination may help repair damaged skin barrier function by restoring reduced FLG expression in keratinocytes. THE THREE HERBAL EXTRACTS INHIBIT IL4–INDUCED IL31 EXPRESSION Th2 lymphocyte-derived cytokines (e.g., IL4 and IL31) transmit the itch sensation by directly activating sensory neurons and blocking IL4 and IL31 signaling by neutralizing antibodies reduces itch in patients with AD (1,44–46). IL31 is considered a crucial mediator of histamine-independent itching (47). Keratinocytes release multiple pruritogenic factors in response to Th2 cytokines (48). However, it is unclear whether keratinocytes express IL31. We tested whether IL4 stimulates IL31 mRNA expression in HaCaT keratinocytes. RT-PCR showed that IL4 enhanced IL31 mRNA expression in a time-dependent manner Figure 4. Effect of the three herbal extracts on FLG subcellular localization in HaCaT cells. HaCaT cells cultured on coverslips were treated with IL4 (20 ng/mL) plus IL13 (50 ng/mL) in the absence or presence of the combination of the three herbal extracts (40 μg/mL A houstonianum, 20 μg/mL B falcatum, and 40 μg/mL S chinensis) for 36 h. After fixing and permeabilization, the cells were incubated with anti-FLG primary, and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibodies (green fluorescence) for immunofluorescence staining. Rhodamine-labeled phalloidin was used as the counterstain for F-actin (red fluorescence). Nuclear DNA was counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue fluorescence). The areas in the dashed boxes are magnified in the right panels. Scale bars, 400 μm.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)