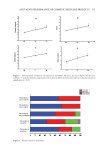
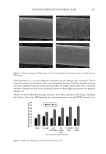
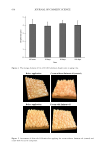
623 Address all correspondence to Yulia Shigabieva, romanovakstu@yandex.ru Liniment of Naftalan Oil: Multifunctional Component for Cosmetic Compositions YULIA A. SHIGABIEVA, SVETLANA A. BOGDANOVA AND ANDREY A. KNYAZEV Department of Cosmetic Technology, Kazan National Research Technological University, 420015, Russia (Y.S., S.A.B., A.A.K.) Accepted for publication October 25, 2021. Synopsis The development of cosmetics with multifunctional biologically active additives of directed action is an area of research. Naftalan oil has a unique complex of therapeutic and cosmetic properties: anti-inflammatory, regenerating, antibacterial, and photoprotective. This work presents the development of cosmetic compositions with liniment of Naftalan oil and the study of their colloidal properties. Liniment of Naftalan oil (Naftin) was included in the formulations of cosmetic compositions—creams, bath foams, and polymer gel. These systems were characterized using a complex of colloidal and sensory methods (organoleptic characteristics, pH measurement, study of rheological properties, foaming, determination of colloidal and thermal stability, and morphology of creams). It was found that the inclusion of liniment of Naftalan oil in the formulation of bath foam increases its foaming ability, and the inclusion in polymer gel leads to a moderate decrease in strength characteristics in optimal concentration range of the active additive that provides uniform application of gel composition. According to optical microscopy, the identity of the facial skin care cream with liniment to the class of multiple emulsions was determined. A pronounced hydrating effect on the skin after applying the cream was revealed. INTRODUCTION Modern compositions of cosmetic and pharmaceutical purposes are a focus of colloidal chemistry research. These are multicomponent heterogeneous systems—emulsions, suspensions, foams, and gels (1–5). Of particular importance in the technologies for their preparation is the introduction of multifunctional biologically active additives into the composition (6–9). Naftalan oil is of particular interest because of its unique complex of medical and cosmetic properties: anti-inflammatory, regenerating, antibacterial, photoprotective, among others (10). In accordance with published data, its high biological activity is due to the presence of naphthenic hydrocarbons in certain fractions (11). Despite extensive use of Naftalan oil for medicinal purposes (12), in the scientific and technical literature there is practically no information about its introduction into the formulation of cosmetics. This work focuses on the development of cosmetic compositions with liniment of Naftalan oil (LNO) and the study of their colloidal properties. J. Cosmet. Sci., 72, 623–632 (November/December 2021)
624 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE MATERIALS AND METHODS SAMPLE COMPOSITION As the active ingredient, LNO Naftin (Naftalan plus, Russia) which is a commercial product and applies without further purification, was used. It is a brown emulsion with a peculiar odor, containing 10 wt% Naftalan oil in water. The basic composition of cosmetic foams included a balanced complex of surfactants, viscosity and acidity regulators, avocado oil, conservation agent, and perfume composition (Table I). Sodium laureth sulfate Texapon® N70 (BASF Company, Germany) and Cocamide DEA Dehyton® PK 45 (BASF Company, Germany) are commercial products that were used without further purification. Gel systems were represented by a polymer gelling agent, moisturizing additive, neutralizing agent, conservation agent, and perfume composition (Table II). Polymer gelling agent TEGO Carbomer 141 was purchased from Evonik (Germany). Cream formulations were based on a complex of structure-forming agents and emollients, emulsifiers, moisturizing and softening additives, conservation agents, and perfume composition (Table III). Stearic acid Kolliwax S, cetearyl alcohol Lanette O, and isopropyl myristate Kollicream IPM were purchased from BASF (Germany) glyceryl stearate TEGIN 4100 Pellets MB were purchased from Evonik (Germany). TEST METHODS The choice of tests for the study of the developed cosmetic compositions was based on the analysis of scientific literature, international standards, and recommendations of the European Cosmetic and Perfumery Association (Colipa) (13–18). Table I Formulation of the Bath Foam With LNO Component Concentration, % Sodium laureth sulfate 20.0 Cocamidopropyl betaine 6.0 Cocamide diethanolamine 3.0 Sodium chloride 2.0 Avocado oil 0.5 Citric acid 0.1 Perfume composition 0.2 Conservation agent 0.1 LNO 0.2–0.9 Deionized water Up to 100.0 Table II Formulation of the Cosmetic Gel With LNO Component Concentration, % Carbomer 0.4 Glycerin 5.0 LNO 0.2–0.9 Triethanolamine 0.2 Perfume composition 0.2 Conservation agent 0.1 Deionized water Up to 100.0
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)