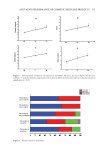
594 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE β-endorphin production and that a combination of the three is more beneficial than each alone. CLINICAL TRIAL TO EVALUATE THE EFFICACY OF THREE HERBAL EXTRACTS FOR ITCHING RELIEF A clinical study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of the combination of three herbal extracts for improving the skin barrier function and soothing itchy skin. The herbal cream was prepared by mixing 2% ethanolic extracts of A houstonianum, B falcatum, and S chinensis with a base cream. Each of the 33 participants either left the area untreated (control group) or topically applied the cream twice daily on the left or right arm. No difference was observed in skin irritation after topical application of the cream (Figure 10A). Self-recorded scores Figure 9. Effect of the three herbal extracts on the suppression of IL4-induced POMC expression in HaCaT cells (A and B). HaCaT cells were treated with IL4 (20 ng/mL) for various time periods (0–36 h). Total RNA was isolated, and POMC mRNA levels were examined by RT-PCR (A) and qPCR (B). GAPDH was used as the loading control. (C) HaCaT cells were treated as in (B), and the concentration of β-endorphin in the culture medium was determined by ELISA. (D and E) HaCaT cells were treated with IL4 (20 ng/mL) for 24 h in the absence or presence of A houstonianum (40 μg/mL), B falcatum (20 μg/mL), S chinensis (40 μg/ mL), or a combination of the three. Total RNA was isolated, and POMC mRNA levels were examined using RT-PCR (D) and qPCR (E). GAPDH was used as the loading control. (F) HaCaT cells were treated as in (E), and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using anti-POMC antibodies. GAPDH was used as the loading control. Relative band intensities were measured using ImageJ. (G) HaCaT cells were treated as in (E), and the concentration of β-endorphin in the culture medium was determined by ELISA. ns: not significant *p 0.05, **p 0.01, ***p 0.001 compared to control (n = 3).
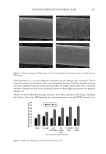
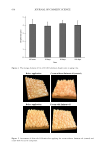
595 SUPPRESSION OF ITCHING BY THREE HERBAL ETHANOLIC EXTRACTS revealed that the degree of itchiness decreased to a statistically significant level (p 0.001) beginning 14 days after topical application of the herbal cream, compared to the untreated control group (Control group: day 0 = 4.76 ± 0.161 day 14 = 4.69 ± 0.163 day 28 = 4.41 ± 0.179. Treatment group: day 0 = 4.89 ± 0.168 day 14 = 3.75 ± 0.224 day 28 = 2.63 ± 0.229 (n = 33)) (Figure 10B). TEWL values significantly decreased (p 0.001) after 28 days (Figure 10C), while skin moisture contents were significantly increased (p 0.001) after 14 days, as compared to the untreated control group (Figure 10D). These results suggest that a combination of A houstonianum, B falcatum, and S chinensis extracts can help improve itching by restoring the skin barrier function. Figure 10. Clinical efficacy of the three herbal extracts on improvements of itchiness and skin barrier function. (A) Representative picture of skin area before and after applying A houstonianum, B falcatum, and S chinensis cream. (B) Cream was applied twice a day in the morning and evening for 28 days. On days 0, 14, and 28, the itch intensity recorded by each subject on a visual analogue scale ranging from 0–10 was expressed as an arbitrary unit (A.U.) (C) Cream was applied as in (B). TEWL was measured using the Tewameter and expressed as 721 g/m2/h. (D) Cream was applied as in (B). The skin hydration content was measured using a Corneometer and expressed as an arbitrary unit (A.U.). A circle indicates the TEWL value of the individual subject. Horizontal lines indicate the mean value (B) or mean + standard error of the mean (C and D) (n = 33). ABS cream: A houstonianum, B falcatum, and S chinensis mixed cream ns: not significant **p 0.01, ***p 0.001.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)