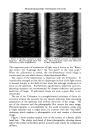
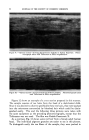
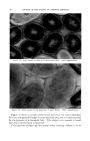
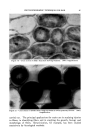
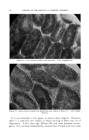
84 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS visible light pass through the altered stratum corneum and reach the level of the melanocytes. Lerner (3) has shown that after a concentrated solu- tion of 8-MOP is irradiated with ultraviolet light a yellow solution is produced. This yellow solution showed absorption in the 4000-6000 Ang- strom range. Pigmentation could be brought about in part by altered 8-MOP and low energy radiation. The dark tanning of the patient who had been using 8-MOP for vitiligo appears to be due to an increased retention of melanin by the pigment- forming cells. Very little is known about the mechanisms controlling the storage or release of pigment after it has been formed by the melano- cyte. Stimulation of the skin by various types of irradiation causes the pigment forming cells to enlarge and probably to multiply. We cannot tell whether enlargement of the melanocytes, a metabolic change causing retention of pigment, or both effects are responsible for the pigment re- tention produced by 8-MOP. INCREASING PIGMENTATION OF NOV, MAt, SKIN Although heat, friction and many types of irradiation will produce pig- mentation, exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the most practical method in use today. When one desires pigmentation of the normal skin, the total melanin content rather than the rate of production is the critical factor. Preliminary evidence indicates that 8-MOP causes an increased retention of pigment by the melanocytes. Lerner stated at the Academy of Dermatology in 1956 that he believed 5-methoxypsoralen produced greater pigmentation with less erythema than did 8-MOP. Bergapten (5-methoxypsoralen) is the photosensitizing principle in oil of bergamot. When this material produces a photodermatitis after application on the skin, there is active pigment formation. The reaction, unfortunately, is so great that it destroys the melanocytes resulting in the deposition of melanin in the cutis. The destruction of the melanocytes is the limiting factor in photosensitization. We cannot say at this time whether or not the pigment retaining effect of the psoralens depends upon photosensitivity. It may be possible to find a chemical in the psoralen group which will produce little photosensi- tivity but relatively great pigment retention. Melanin may be retained in the stratum comeurn after it has left the melanocyte. Many people experience the loss of their suntan as soon as they start to peel. The altered stratum comeurn produced by 8-MOP is very adherent and it does not peel. Therefore 8-MOP produces reten- tion of melanin both in the melanocytes and in the horny layer. Any procedure such as the application of a mild acid which hardens the horny layer and makes it adherent will prolong a suntan.
METHODS OF INCREASING SKIN PIGMENTATION 85 INCREASING PIGMENTATION IN VITILIGO Vitiligo is a disease where the melanocytes produce no pigment. The cause of the inhibition of tyrosinase is not known. Tyrosinase is nor- mally partially inhibited. I do not feel that vitiligo represents an in- crease in normal inhibition, but that another inhibitory mechanism is involved. Therapy in vitiligo is directed solely at the release of tyrosinase with resulting pigment production. Almost all therapy for vitiligo produces inflammation and, the greater the inflammation, the better the results. Vibra-Puncture, Croton oil (4), 8-MOP and sunlight, electrolysis to the point of crusting followed by copper sulfate have been used to treat vit- iligo. This type of treatment is not good therapy. A general irrita- tion of the skin is produced to obtain the freeing of one enzyme. There has been one preliminary report which may point the way to a better method of treating vitiligo. Christiansen (5) gave a patient with vitiligo chloroquine diphosphate to protect him against sunburn. After prolonged exposure to sunlight, repigmentation developed. It may be possible to find an anti-inflammatory chemical which will prevent the nonspecific inflammation from sunlight while allowing the ultraviolet energy to free the enzyme tyrosinase. ACCESSORY FACTORS Tyrosinase is a copper protein and inactivation of the copper stops the function of the enzyme. ¾oshida (6) has found that copper sulfate alone may activate tyrosinase. El-Mofty (7) has given copper sulfate by mouth to patients using 8-MOP and sunlight claiming to have increased the cure rate in vitiligo. It would appear that copper has a place as a thera- peutic aid in producing pigmentation. HORMONES The melanocyte stimulating hormone of the pituitary will produce pig- mentation. There are probably other hormones that act in conjunction with this factor but their mechanism of action, physiological balance and possible deleterious effects have not been elucidated. SUMMARY The normal pigmenting cycle is discussed. Preliminary work on the actual changes produced by 8-methoxypsoralen are presented. The pres- ent therapy used to produce pigmentation is discussed with possible im- provements in these agents. BIBLIOGRAPHY (1) Becker, S. W., Jr., Fitzpatrick, T. B., and Montgomery, H., ?lrch. Dermatol. and Syphilol., 65,511 (1950).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)