KINETICS OF DEGRADATION OF PARABENS 497 determined at 253 nm, the wavelength of maximum absorbance, using chloro- form as the blank. A Beeifs law relationship was obtained for methyl, ethyl, propyl, and n-butyl paraben in chloroform at 253 nm. Method of Analysis The following general procedure was developed and used for stud,ving the effects of various factors, i.e., pH, temperature, ionic strength, on the rate of hydrolysis of the parabens. An accurately weighed quantity of paraben was added to a 100-ml volumet- fie flask and dissoIved in a small volume of appropriate buffer solution with the aid of heat. The solution was diluted to volume with the buffer solution which had been preheated to the temperature at which the particular analysis was made. The flask was placed in a constant temperature eirculator bath that had been previously adjusted to the desired temperature (-0.1øC). The solution was allowed to thermally equilibrate for 10 min, then a 5-ml aliquot, representing the zero hour sample, was withdrawn and transferred to a separatory funnel which contained g0 ml of chloroform. At pH 9.0, p- hydroxybenzoie acid (pK• 4.48) exists as a salt which remained in the aqueous phase when the solution was extracted with chloroform. Complete extraction of the unclecomposed paraben was accomplished using 3 x 20 ml of chloroform extractions. The combined chloroform extracts were filtered into a 100-ml volumetric flask through filter paper that had been previously wetted with chloroform. The solution was diluted to volume with chloroform, and the absorbance was determined at 253 nm using chloroform as the blank. Samples were removed at definite time intervals and analyzed by this procedure. Since p-hydroxybenzoie acid is the major degradation product of hydrolysis of the parabens (1, 9), mixtures containing known concentrations of methyl, ethyl, propyl, and n-butyl paraben and p-hydroxybenzoic acid were prepared. The ester concentration in each mixture was determined using the extraction procedure previously described. The per cent recovery of the parabens alone and in combination with varying concentrations of p-hydroxybenzoic acid is shown in TabIe I. The initial concentration of each paraben in all subse- quent studies was 5 rag/1. pH and Temperature Effects In order to study the effect of pH and temperature on the rate of hydrolysis of methyl, ethyl, propyl, and n-butyl paraben, the reactions were carried out at three temperatures in buffer solution as follows: 70øC-pH 2.75, 3.66, 4.58, 5.49, 6.41, 7.33, 8.24, and 9.16 50øC-pH 9.16 40øC-pH 9.16. Reactions were carried out for a maximum of 160 hours, and all aliquots were analyzed using the extraction procedure described above.
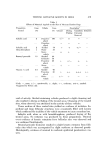
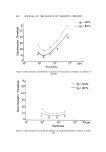
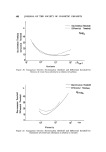
498 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I Recovery of Paraben from a Mixture of Paraben and p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Composition of Mixture (mg/l.) Amount of Paraben Paraben Acid Found (mg/1.) % Recovery Methyl Paraben 503 0.00 4.95 98.4 4.02 1.03 4.05 100.7 3.02 2.06 3.00 99.3 2.01 2.58 2.03 100.9 1.01 5.16 0.98 97.0 Ethyl Paraben 4.66 0.00 4.70 100.9 3.73 1.03 3.70 99.2 2.80 2.06 2.77 98.9 1.86 2.58 1.85 99.5 0.93 5.16 0.95 102.2 Propyl Paraben 5.31 0.00 5.40 101.7 4.25 1.03 4.22 99.3 3.19 2.06 3.20 100.3 2.12 2.58 2.10 99.1 1.06 5.16 1.07 100.9 n-Butyl Paraben 5.29 0.00 5.30 100.2 *$.23 1.03 4.12 97.4 3 17 2.06 3.17 100.0 2.12 2.58 2.05 96.7 1.06 5.16 1.10 103.8 Effect of Paraben Concentration Solutions of methyl, ethyl, propyl, and n-butyl paraben were prepared at at 70øC in 0.0005-0.20M phosphate buffer at pH 8.24 and constant ionic strength of 0.3, and the hydrolysis was followed at 70øC in the manner previously described. Effect of Ionic Strength The effect of ionic strength on the hydrolysis of the parabens was investi- gated by studying the hydrolyric rate, at 70øC, of paraben soluti.ons in 0.1M phosphate buffer at pH 8.24. The buffers were adiusted to ionic strengths of 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, and 1.2 by the addition of potassium chloride. The effect of buffer concentration on hydrolytic rate was also studied by following the hydrolysis at 70øC in 0.005-0.20M phosphate buffer at pH 8.24 and constant ionic strength of 0.6.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)