RESIDUAL ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY ON HUMAN SKIN 419 The plate counts were found to be remarkably similar among the subjects across the 4 treatments. The average plate counts on the incubated controls were almost identical to the counts obtained from the areas treated with Ivory soap. An analysis of variance showed that there was no significant difference in the responses among the subjects to each treatment. After 24 hours, with no additional application of test materials, the areas were washed thoroughly for i rain with water-soaked gauze pads and seeded plates applied. The results of this phase are shown in Table II. Dial soap may have maintained some activity on day two. Both pHisohex and HyperpHaze-treated areas were still quite active. The process was re- peated 24 hours later, and the results are shown in Table III. The areas of the arms treated with Ivory soap, Dial soap, and pHisohex had lost all of their activity while the area treated with HyperpHaze was still ca- pable of lowering the count by 21%. This result was significant at the o• = .01 level. This study was repeated using a larger number of subjects. Sixteen males participated in the experiment, and the results obtained are shown in Table IV. Day One An analysis of variance indicated a significant difference beyond P equals 99. A Student-Newman-Keu]s (8) test was then run to determine where the differences occurred and at what level of significance. This resulted in the following conclusions. 1. There is no significant difference bet•veen the average counts of the controls put directly into the incubator and plates from the sites washed with Ivory soap. 2. All other average counts differ from each other at the 99 per cent level of significance. The conclusions to be drawn from these data are that Ivory soap leaves no antibacterial residue on the skin. Dial, pHisohex, and HyperpHaze do leave a residue with the following order of effectiveness: HyperpHaze pHisohex Dial soap. Day Two After scrubbing the treated sites thoroughly with water, fresh plates were applied. The results of this phase are shown in Table V. The analysis of variance indicated, again, a significant difference beyond P equals 99. The Student-Newman-Keuls test revealed the following. 1. There are no significant differences among the control, Dial, and Ivory soaps.
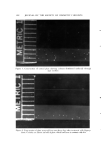
420 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table V Results Obtained on Day Two Number of Average Number Standard Per cent Change Test Material Observations of Bacteria/Plate Deviation vs. Control Ivory soap 16 265.3 16.29 q- 1.2 Dial soap 16 263.0 16.22 q- 0.4 pHisohex 16 226.8 15.06 --13.5 HyperpHaze 16 182.0 13.49 --30.5 Control 15 262.1 16.19 - 2. Hyperpttazc and pHisohex differ from the control, Dial, and Ivory soap at the 99% level of significance. 3. The 30.5% decrease in the counts obtained with HyperpHaze is sig- nificantly different from the 13.5% decrease obtained with pHisohex at the 99% level of significance. It is evident, therefore, that 24 hours after a single application of the test solutions, residual activity of Dial soap against S. epidermidis is gone. It is also apparent that, while the activity of the other two treated areas has decreased, the HyperpHaze-treated sites retain more activity against the test organism than do the sites treated with pHisohex. Day Three The same procedure was follo ved as for Day two and results were obtained as is shown in Table VI. The analysis of variance followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test indi- cated that there were no significant differences among the counts obtained from the controls placed in the incubator and the sites exposed to Ivory soap, Dial soap, and pHisohex, while the counts on the plates from the area treated with HyperpHaze were significantly lower than the other 4 groups at the 99% level. The results of this experiment imply, therefore, that the residual activity of pHisohex is gone on the last day and a small, but meaningful, amount of activity remains on areas treated with the HyperpHaze solution. It can also be concluded that for every day of the test, HyperpHaze-treated areas were ca- pable of inhibiting the growth of more S. epidermidis eelIs than sites treated with any of the other preparations tested. These results were found to be highly significant each day. Examination of the HyperpHaze plates h'om day three reveals that the surviving organisms are in the lower portion of the plates, while the upper parts are free of visible colonies. Examination of cross-sections of these plates
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)