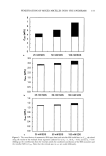
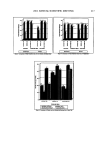
128 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 2O E15 .o_ 10 o 5 0 0 lO 8 , Rovisome © + vitamin E-acetate results by HPLC UV spectroscopic results with 2 x standard deviatio A results by HPLC UV spectroscopic results with 2 x standard deviation B -20 i tape strip number Figure 5. Results (one udder study) performed by spectroscopy (mean, 2 x SD) and the HPLC method (mean) at the exposure periods of 0.5 h (A) and 1.5 h (B) for the Rovisome © cream formulation. DISCUSSION The aim of this i, vitro study was to test the applicability of UV/VIS spectroscopy in order to facilitate the analytical procedure of a large number of horny layer samples, usually analyzed by HPLC. In the case of the BUS model the loaded strips exhibit a large representative area (19 cm 2) of the horny layer. Generally, compared to human adhesive tape stripping, the size of the tapes used is significantly increased. Therefore, the logistics and the manipulation of several hundred strips during chemical analysis are labor-intensive. Transmission spectroscopy is much easier and faster and can at least halve the costs. The results indicate that the choice of five spots loaded with corneocytes and avoiding lower loaded or empty spots are appropriate. Except for the case of the first tape, the
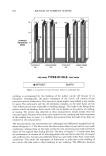
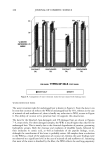
VITAMIN E ACETATE PENETRATION STUDIES 129 -- 20 •=•=•=•=•=z•=•=•z-•=•=•=•=•=•-------•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•=•===•==•==•==•=•=•==•=•=•-- o stri::i!.:'i•?.--"'..'":l::iiii'"'"•"•:•'":• :--... ' '"'"'"'•'"•"'""'"'"•:'•':•::•:••••!•i •ii•:•jjj•i•:•ii:i!•i•`•`•:••••i•:• '"'"' ":4•'.."4:ii•iii•':'"::•3.....'".'.'•i• i•i?•:•j•ii•:•:•:•:•i•i•:•:•:•: ::•:•i•:i•::• ::•"::'v'•:..•. Tapes containing fractional vitamin E acetate contributing to total SO-penetrated amount • Results by UV-Spectroscopy • HPLC-results Figure 6. Results (lag/cm 2) of vitamin E acetate determination by spectroscopy and the HPLC method after adhesive tape application. Amounts from LC, RP, and RS formulations found in various strips after exposure periods of 0.5 h (A) and 1.5 h (B), respectively. results of both methods are quite comparable. The result of the first tape may be artefactual due to the entrapped material that was not completely removable. For the HPLC method the whole strip was used, whereas for the spectroscopic assay only strip locations were evaluated. However, for both methods a higher accuracy can be achieved by quantifying the individual number of corneocytes sticking to the tape. The BUS-irritation assay differentiates biochemically between activation/reversible in- jury or death of epidermal cells using whole skin biopsies. Therefore, rubbing or strip- ping the skin induces a reversible activation of epidermal cells, e.g., an increase of the arachidonic acid metabolism, but no cytotoxic action to keratinozytes at all (unpublished results). There are also anatomical differences between irritancy (reversible injury) and cytotoxicity. In reconstructed human skin equivalents (RE-DED cultures) it was shown that the MTT-positive cells could be attributed to the lower cell layers, whereas the terminally differentiated keratinozytes may not be involved (12). In this irritation study with three cream formulations, no difference was observed for the cytotoxic activity, which usually occurs in the basal and suprabasal epidermal cells. Neither type of for- mulation was able to alter the activity of the basic cream under exposure conditions of 60 minutes from the beginning. The results only indicate biological activity regarding the arachidonic acid metabolism that was more active by using Rovisome © as liposomal carrier than by using microparticles or the liposome-free cream. This indicates activation but no irritation of the upper epidermal cells that may contribute to the high uptake of vitamin E acetate into the horny layer under short-term exposure. Vitamin E acetate in Rovisome © as liposomal carrier delivered most of the bioactive substance into the skin, compared to other formulations such as the lameliar cream (LC) or a microparticle-based one (Roviparts©). The reasons for the difference can be explained
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)