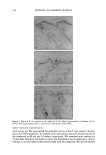
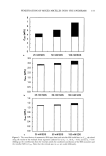
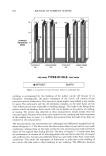
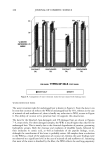
PENETRATION OF MIXED MICELLES INTO THE EPIDERMIS 157 is a direct correlation between the CMC and the observed skin irritation. However, preventing the micellar SDS, or for that matter any miceliar surfactant, from penetrating into the skin has a pronounced effect on skin irritation, because it should eliminate the dose-dependent behavior commonly observed for pure surfactant systems (2,3,8,13,16,18). Once the micelies are prevented from penetrating into the skin, the only other mechanism to reduce C•i, involves a reduction in the surfactant toohomer concentration. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank Hua Tang for numerous useful discussions about the preparation of skin samples and other experimental details, as well as on hindered-transport theories. We also thank Allison Fielder for her assistance in developing the surfactant skin penetration technique. We are grateful to Unilever Home and Personal Care NA for financial support for this work. Peter Moore thanks the Natural Sciences and Engineering Re- search Council of Canada for the award of a PGS-B scholarship. REFERENCES (lO) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (1) W. Abraham, "Surfactant Effects on Skin Barrier," in Surfactants in Cosmetk•, M. M. Rieger and L. D. Rhein, Eds. (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1997), pp. 437-487. (2) K. I. Cumming and A.J. Winfield, In vitro evaluation of a series of sodium carboxylates as dermal penetration enhancers, Int. J. Pharm., 108, 141-148 (1994). (3) J. A. Faucher and E. D. Goddard, Interaction of keratinous substrates with sodium lauryl sulfate II. Permeation through stratum corneum, J. Soc. Cosmet. Ch•z., 29, 339-352 (1978). (4) C.L. Froebe, F.A. Simion, L.D. Rhein, R.H. Cagan, and A. Kligman, Stratum corneum lipid removal by surfactants: Relation to in vivo irritation, Dermatologica, 181, 277-283 (1990). (5) S. E. Friberg, L. Goldsmith, H. Suhaimi, and L. D. Rhein, Surfactants and stratum corneum lipids, Colloids Surf, 30, 1-12 (1988). (6) T.J. Hall-Manning, G. H. Holland, G. Rennie, P. Revell, J. Hines, M.D. Barratt, and D. A. Bas- ketter, Skin irritation potential of mixed surfactant systems, Fd. Chem. Toxic., 36, 233-238 (1998). (7) I. Hama, H. Sasamoto, T. Tamura, T. Nakamura, and K. Miura, Skin compatibility and ecotoxicity of ethoxylated fatty methyl ester nonionics, J. Surf Det., 1, 93-97 (1998). (8) C. H. Lee and H. I. Maibach, Study of cumulative irritant contact dermatitis in man utilizing open application on subclinically irritated skin, Contact Dermatitis, 30, 271-275 (1994). (9) K. D. Peck, J. Hsu, S. K. Li, A.-H. Ghanem, and W. I. Higuchi, Flux enhancement effects of ionic surfactants upon passive and electroosmotic transdermal transport, J. Pharm. Sci., 87, 1161-1169 (1998). L.D. Rhein, C. R. Robbins, K. Fernee, and R. Cantore, Surfactant structure effects on swelling of isolated human stratum corneum, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 37, 125-139 (1986). K.-P. Wilhelm, G. Freitag, and H. H. Wolff, Surfactant-induced skin irritation and skin repair,J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 30, 944-949 (1994). H. Tang, S. Mitragotri, D. Blankschtein, and R. Langer, Theoretical description of transdermal transport of hydrophilic permeants: Application to low-frequency sonophoresis, J. Pharm. Sci., 90, 545-568 (2001). T. Agner and J. Serup, Sodium lauryl sulphate for irritant patch testing•A dose-response study using bioengineering methods for determination of skin irritation, J. Invest. Dermatol., 95, 543-547 (1990). J. Vilaplana, J. M. Mascaro, C. Trullas, J. Coll, C. Romaguera, C. Zemba, and C. Pelejero, Human irritant response to different qualities and concentrations of cocoamidopropylbetaines: A possible model of paradoxical irritant response, Contact Dermatitis, 26, 289-294 (1992). K.-P. Wilhelm, M. Samblebe, and C.-P. Siegers, Quantitative in vitro assessment of N-alkyl sulphate-
158 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE (25) (26) (27) (28) (29) (30) (31) (32) (33) (34) (_35) (36) (37) (38) induced cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes (HaCaT): Comparison with in vivo human irritation tests, Br. J. DermatoL, 130, 18-23 (1994). (16) K.-P. Wilhelm, A. B. Cua, H. H. Wolff, and H. I. Maibach, Surfactant-induced stratum corneum hydration in vivo: Prediction of the irritation potential of anionic surfactants,J. Invest. Dermatol., 101, 310-315 (1993). (17) C. Szolar-Platzer, S. Patil, and H.I. Maibach, Effect of topical laurocapram (Azone ©) on the in vitro percutaneous permeation of sodium lauryl sulfate using human skin, Acta Derre. VenereoL, 76, 182-185 (1996). (18) M. Loden, The simultaneous penetration of water and sodium lauryl sulfate through isolated human skin, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 41, 227-233 (1990). (19) A.D.1. Maza, L. Coderch, O. Lopez, J. Baucells, and J.L. Parra, Permeability changes caused by surfactants in liposomes that model the stratum corneum lipid composition,JOACS, 74, 1-8 (1997). (20) J. L. Zatz and B. Lee, "Skin Penetration Enhancement by Surfactants," in S•rfactants in Cosmetics, M. M. Rieger and L. D. Rhein, Eds. (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1997), pp. 501-517. (21) G. Imokawa, K. Sumura, and M. Katsumi, Study on skin roughness caused by surfactants. II. Cor- relation between protein denaturation and skin roughness, JOA CS, 52, 484-489 (1975). (22) P. Thau, "Surfactants for Skin Cleansers," in Surfactants in Cosmetics, M. M. Rieger and L. D. Rhein, Eds. (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1997), pp. 285-306. (23) A.D.1. Maza, J. Baucells, P. Gonzalez, and J. L. Parra, Sublyric effects caused by C•4-alkyl betaine/ sodium dodecyl sulfate mixtures in liposomes modeling the stratum cometun lipid composition, Colloids Surf A, 133, 253-260 (1998). (24) L. D. Rhein, F. A. Simion, R. L. Hill, R. H. Cagan, J. Mattai, and H. I. Maibach, Human cutaneous response to a mixed surfactant system: Role of solution phenomenon in controlling surfactant irrita- tion, Dermatologica, 180, 18-23 (1990). K. P. Ananthapadmanabhan, C.L. Meyers, and M.P. Aronson, Binding of surfactants to stratum corneum, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 47, 185-200 (1996). L. Rigano, T. Cavalletti, S. Benetti, and S. Traniello, Evaluation of predictable irritative power of surfactant mixtures by human fibroblast culture and its correlation to physico-chemical parameters, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 17, 27-43 (1995). M.J. Rosen, Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 2nd ed. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1989). P. Moore, S. Puvvada, and D. Blankschtein, Challenging the surfactant monomer skin penetration model: Penetration of sodium dodecyl sulfate micelies into the epidermis, J. Cosmet. Sd., 54, 29-46 (2003). J. A. Faucher and E. D. Goddard, Interaction of keratinous substrates with sodium lauryl sulfate. I. Sorption, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 29, 323-337 (1978). A. Shiloach and D. Blankschtein, Predicting miceliar solution properties of binary surfactant mixtures, Langmuir, 14, 1618-1636 (1998). A. Shiloach and D. Blankschtein, Measurement and prediction of ionic/nonionic mixed micelle for- mation and growth, Langmuir, 14, 7166-7182 (1998). A. Rohde and E. Sackman, Quasieleatic light-scattering studies of miceIlar sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions at the low concentration limit, J. Colloid. Interface Sci., 70, 494-505 (1979). P.J. Missel, N. A. Mazer, G. B. Benedek, and M. C. Carey, Influence of chain length of the sphere- to-rod transition in alkyl sulfate micelles, J. Phys. Chem., 87, 1264-1277 (1983). P. L. Dubin, J. H. Grubher, J. Xia, and H. Zhang, The effect of cations on the interaction between dodecylsulfate micelles and poly(ethyleneoxide),J. Colloid. Interface Sci., 148, 35-41 (1992). L. Magid, "Light Scattering in MiceIlar Systems," in Dynamic Light Scattering: The Method and Some Appli•tionJ, W. Brown, Ed. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1993), pp. 554-593. A. Einstein, InveJtigation on the Theory of Brownian Movement (Dover, New York, 1956), p. 58. W. Brown, J. Fundin, and M. G. Miguel, Poly(ethylene oxide)-sodium dodecyl sulfate interactions studied using static and dynamic light scattering, MacromolecMes, 25, 7192-7198 (1992). A.d. Nardo, K. Sugino, P. Wertz, J. Ademola, and H. I. Maibach, Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) induced irritant contact dermatitis: A correlation study between ceramides and in vivo parameters of irritation, Contact Dermatitis, 35, 86-91 (1996). (39) H. Korting, T. Herzinger, A. Hartinger, and M. Kerscher, Discrimination of the irritancy potential of surfactants in vitro by two cytotoxicity assays using normal human keratinocytes, HaCaT cells and 3T3 mouse fibroblast: Correlation with in vivo data from a soap chamber assay, J. Dermatol. Sci., 7, 119-129 (1994).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)