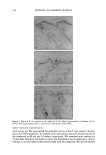
PENETRATION OF MIXED MICELLES INTO THE EPIDERMIS 159 (40) A.d. 1. Maza and J. L. Parra, Subsolubilizing effects of alkyl sulfates on liposomes modeling the stratum. corneum lipid composition, Langmuir, 12, 6218-6223 (1996). (41) P. v. d. Valk, J. Nater, and E. Bleumink, Skin irritancy of surfactants as assessed by water vapor loss measurements,J. Invest. Dermato/., 82, 291-293 (1984). (42) J. R. Welty, C. E. Wicks, and R. E. Wilson, Fundamentals of Momentum, Heat, and Mass Transfer, 3rd ed. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1984). (43) K. D. Peck, V. Srinivasan, S. K. Li, W. I. Higuchi and A.-H. Ghanem, Quantitative description of the effect of molecular size upon electroosmotic flux enhancement during iontophoresis for a synthetic membrane and human epidermal membrane, J. Pharm. Sci., 85,781-788 (1996). (44) P. M. Lai and M. S. Roberts, An analysis of solute structure-human epidermal transport relationships in epidermal iontophoresis using the ionic mobility: Pore model, J. Controlled Release, 58, 323-333 (1998). (45) S. K. Li, W. Suh, H. H. Parikh, A.-H. Ghanem, S.C. Mehta, K. D. Peck, and W. I. Higuchi, Lag time data for characterizing the pore pathway of intact and chemically pretreated human epidermal mem- brane, Int. J. Pharm., 170, 93-108 (1998). (46) D. F. Evans and H. Wennerstrom, The Colloidal Domain Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Technology Meet. Advances in Interfacial Engineering Series, E. Cohen and E. Gutoff, Eds. (VCH Publishers, New York, 1994). (47) W. M. Deen, Hindered transport of large molecules in liquid-filled pores, AIChEJ., 11, 1306-1314 (1987).
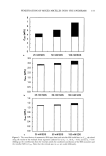
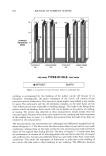
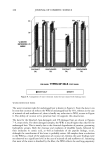
J. Cosmet. Sci., 54, 161-174 (March/April 2003) Effect of formulation on the topical delivery of o-tocopherol MEERA RANGARAJAN and JOEL L. ZATZ, Organon USA, 3 75 Mt. Pleasant Avenue, West Orange, NJ 07052 (M.R.), and Laboratory of Cancer Research, Rutgers University, 41-D Gordon Road, Piscataway, mJ 08854 (J.L.Z.). Accepted for publication August 19, 2002. Synopsis The objective of this research was to investigate the effect of concentration and delivery system on skin permeation of (x-tocopherol ((x-T). Also, the addition of sunscreens and oleic acid on (x-T permeation was studied using an in vitro micro-Yucatan pig skin model. Various delivery systems of (x-T (1%) were formulated, which included simple solution, gels, emulsions, and microemulsions. The experimental design chosen for this study was a statistical randomized complete block design. (x-T delivery was proportional to its concentration. The hydroalcoholic gel delivered significantly higher amounts of (x-T into the receptor than the other gels used. A microemulsion containing isopropyl myristate emerged as the best delivery system for (x-T among all the systems studied. Pig skin is a suitable in vitro model for studying the permeation of (x-T and possibly other antioxidants, though in vivo experiments in humans are required to further corroborate the data. INTRODUCTION Research has shown that UV radiation damages DNA and genetic material, oxidizes lipids and produces harmful free radicals, causes inflammation that also produces free radicals, disrupts cell communication, causes expression of stress response genes, and weakens the immune response of the skin. o•-Tocopherol (o•-T) is the major lipophilic antioxidant in many biological systems (1). Topical application of o•-T has been shown to protect against UV-induced cutaneous damage, carcinogenic and mutagenic activity of ionizing radiation, and chemical agents (2). o•-T has been found to reduce tumor incidence in mice (3) and decrease fine lines, wrinkles, and sagging induced by photo- aging (4,5). o•-T is now considered essential for the stabilization of biological mem- branes, particularly those containing large amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The oxidation of unsaturated fats produces lipid peroxides, which interfere with the structure and function of biological membranes. When dl-o•-tocopherol was added to commercial Address all correspondence to Meera Rangarajan. 161
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)