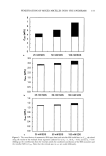
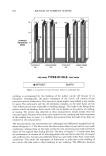
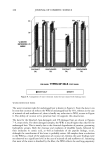
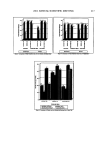
198 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE shown in Figures I and 2. Figure 1 shows the results for the set of runs where long-chain PEG was incorporated into the elastomer. All of these PEG-DCP samples had relatively low viscosity, except for the sample where the PEG substitution level and crosslink density were both low. When the PEG-DCP was prepared using short-chain PEG, the results shown in Figure 2 indicate that crosslink density had a larger effect on the viscosity of the dispersion. It should be noted that the central data point shown in Figures 1 and 2 (medium PEG substitution level and medium crosslink density process parameter) corresponds to a PEG-DCP made at the midpoint for all three process variables (including PEG chain length). This is a consequence of the experimental design that calls for multiple runs at the "center point" of the variables being studied. The water-uptake results are shown in Figures 3 and 4. All of the PEG-DCP samples made with long-chain PEG were effective emulsifiers, producing water uptake values of greater than 70%. Water uptake for the PEG-DCP runs with short-chain PEG, shown in Figure 4, were somewhat lower. The sample made with the minimum PEG substi- tution level and high crosslink density had the worst emulsification efficiency, with a water-uptake value of only 25 %. Overall, the PEG-DCP runs where the long-chain PEG was used produced the most effective emulsifiers. When PEG-DCP was made with short-chain PEG, the best emulsifiers were made with the high level of PEG substitu- tion. The water-uptake values were initially measured for PEG-DCP dispersions that con- tained 9% by weight of the elastomer. The water-uptake test was repeated for disper- sions that were diluted (with cyclopentasiloxane) to 7% and 5%. For the PEG-DCP sample made with long-chain PEG, dilution did not have a large effect on water uptake. For two of the PEG-DCP samples made with short-chain PEG, dilution dramatically increased the water uptake, as shown in Figure 5. This dilution effect may be due to the elastomer assuming a more extended configuration at lower concentrations. Emulsions made with the diluted PEG-DCP samples appear to be just as stable as those made with the original PEG-DCP samples (9% elastomer). EVALUATION OF PEG-DCP IN ANTIPERSPIRANT GEL One of the largest commercial applications for w/s emulsions where the continuous phase -- 160000. 140000 120000 100000 Viscosity 80000. • (cP) 60000 40000 20000 Low Medium High Crosslink 0 Density " Process High Medium Parameter Low PEG Substitution Level Figure 1. The effect of PEG substitution level and crosslink density process parameter on the viscosity of PEG-DCP made with long-chain PEG.
HYDROPHILICALLY MODIFIED SILICONE ELASTOMERS 199 Viscosity (cP) 160000ß 140000,- 120000- 100000 • 80000 ß 60000--' 40000 Y 20000 ß Low Crosslink 0 " ' '•'"• Medium Density High Process High Medium Parameter Low PEG Substitution Level Figure 2. The effect of PEG substitution level and crosslink density process parameter on the viscosity of PEG-DCP made with short-chain PEG. 90 Y, 80' 70=, 60" Water Uptake 50 (wt %) 40:: 30 •: 20 lO 0.•', High Medium PEG Substitution Level Low Crosslink Medium Density High Process Parameter Low Figure 3. The effect of PEG substitution level and crosslink density process parameter on water uptake for PEG-DCP based on long-chain PEG. consists primarily of cyclomethicone (cyclotetrasiloxane and/or cyclopentasiloxane) is in antiperspirant gels. In these products, the water phase consists of an aqueous solution of antiperspirant salt, and often the refractive index of the water and silicone phase are matched to produce a transparent emulsion. For our investigation, we compared a commercial silicone emulsifier, PEG/PPG-18/18 dimethicone (Dow Corning © 5225C Formulation Aid), with two elastomeric emulsifiers. The first was similar to the PEG- DCP samples discussed previously. It was made with a high level of PEG substitution and low crosslink density. For the other elastomeric emulsifier, we used a copolymer of polyethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol (PEG/PPG) as the hydrophilic group in order to make it more similar to the dimethicone copolyol emulsifier. This second type of elastomeric emulsifier is referred to as PEG/PPG-DCP. Both elastomeric emulsifiers produced stable antiperspirant gels. Figure 6 shows the viscosity for the gels based on the elastomeric emulsifiers and the PEG/PPG-18/18
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)