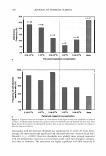
CHLORINATED BACTERIOSTATS z -..., a) b) 0 2 4 6 8 IO 12 Time (min) 189 Figure 3. Separation of mixture of (a) triclocarbon and (b) triclosan. Stationary phase: Nucleosil C 18 (4.6 x 250 mm). Mobile phase: acetonitrile/water (70:30, v/v). Flow rate 1.5 ml/min, injection 200 µl. RI temperature: 39 ° C. Table II Recoveries of Triclosan and TCC From Spiked Samplesa Triclosan TCC Amount added Found Recovery Amount added Found Recovery Samples (weight %) (weight %) (%) (weight %) (weight %) (%) Toothpaste 0.024 0.024 101 (3.4%i' Deodorant stick 0.120 0.121 101 (5.6%) Anti-acne washing cleanser 0.120 0.126 105 (0.5%) Antibacterial body wash 1.00 X 10- 3 0.988 X 10- 3 99 (3.6%) a Number of determinations (n = 3). 6 Relative standard deviation. foam shower bath liquid is shown in Figure 4. Solid electrodes include various types of carbon and different noble metals. Glassy carbon electrode (GCE) is the most widely used carbon electrode material. It is inert to common organic solvents and has a wide potential range (from - 1.0 to + 1.3 V). Examination of the triclosan structure shows that
190 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE ..., z ...... a) b) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Time ( min) Figure 4. Chromatogram obtained from commercial foam shower bath liquid. (a) triclocarbon. (b) triclosan. this compound may undergo oxidation at a GCE. A well-defined anodic peak appeared at +0.46 V versus SCE, and the magnitude of the peak current appeared to be propor- tional to concentration. However, an anodic peak for TCC that was not electrooxidation- active was not found. The electrochemical reduction of organic halogen involves cleavage of the carbon-halogen bond in a single two-electron polarographic wave to give a carbanion, which is subsequently protonated (29). The function of the ether group is to make removal of electrons from the aromatic system occur more readily, and Stackelberg and Stracke proposed the mechanism RX + 2e - ➔ R - + x- � RH + x-. According to the log plot slope, the reduction is irreversible (30). Aromatic halides are more difficult to reduce than alkyl halides, but the process is still a two-electron reduction, to replace the halogen by hydrogen (31). Mercury and lead as electrode materials offer the wider cathodic potential range, and thus they are commonly used for the reducible species. Mercury and lead-coated gold or glassy carbon electrodes can also be employed. The reduction of TCC and triclosan in 0.1 mol 1- 1 tetrabutylammonium hydroxide was studied on GCE, a thin-film mercury deposited on GCE (TFME), and a thin-film lead deposited on GCE (TFLE). It was found that TFME and TFLE gave a
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)