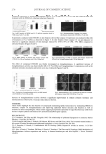
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 246 increases, the more the cosine of this angle becomes small or even negative, and therefore the more the interfacial tension of the interface solid/liquid is important. Conversely, the more the contact angle decreases, the more the interfacial tension of the interface solid/ liquid also decreases. Wettability measurements. Wettability of untreated and pre-treated HD6 was tested by deionized water to evaluate the properties of the surface and the variation brought by the amphoteric treatment. Then the contact angles (θ) formed after the deposition of A and B on the HD6 with and without pretreatment were measured to compare the interfacial tension of both products according to the substrate properties. Measurements were performed by the Laboratory of Chemistry of Organic Materials and Metal, University of Nice-Sophia Antipolis. The contact angles (θ) were measured by a goniometer (Krüss DSA-10 contact angle goniometer). Drops of water and cream were deposited using a syringe controlled by a computer (fi xed volume) on the surface of the HD6 plate. The contact angle was determined from images captured by the computer via a camera (software drop shape analysis). SURFACTANT SELECTED FOR HD6 PRETREATMENT, COCAMIDOPROPYL BETAIN The amphoteric surfactant, cocamidopropyl betain (C.B.) (Figure 2) was selected as a pretreatment to decrease the hydrophobicity of the HD6 PMMA plates. (commercial name: TEGO® Betain F50). Supplied by Evonik Goldschmidt Industries, cocamidopropyl betain is more highly concentrated than common products incorporating 30% of raw material (13). IN VITRO SPECTROSCOPIC MEASUREMENTS ON HD6 AND PRETREATED HD6 All the spectroscopic data used in this study were based on transmission measurements of suncare products applied on HD6 with or without amphoteric pretreatment. The transmission spectrum for each area measured was determined, and then absolute protection factors like SPF were calculated by combining the UV transmission spectrum of the sun- screen preparation with a specifi c biological action spectrum and a relevant sun emission spectrum. Operating conditions. A Labsphere® UV-2000 S Transmittance analyzer was used in the deter- mination of the diffuse transmission spectrum of UV radiation through the substrate Figure 2. Chemical structure of cocamidopropyl betain. A. aliphatic tail. B. Polar head.
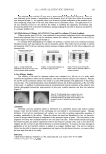
IN VITRO SPF DETERMINATION ON HD6 PMMA 247 before and after application of the sunscreen. A PMMA plate covered with 10 mg of C.B. was used to obtain the blank transmittance spectrum from 290 to 400 nm in steps of 1 nm. Preliminary studies showed that the optimal amount of sunscreen per surface unit on these high-roughness plates is 1.3 mg/cm2 (5). Twelve milligrams of C.B. were spread with a saturated fi ngercot until a homogenous dis- tribution was achieved over the whole surface. A period of ten minutes is necessary for C.B. stabilization. Samples A and B were applied in parallel on the HD6 PMMA with and without C.B. pretreatment. The sunscreen product was spread over the whole surface by means of light strokes with a fi ngertip “presaturated” with the product. The different formulae studied were spread with the same protocol. The sample thus obtained was allowed to settle for 15 minutes in the dark at room temperature to ensure a leveling of the formula. A total of 9 UV trans- mission spectra (from 290 to 400 nm, 1-nm increment steps) were recorded on each plate at different locations. ROUGHNESS MEASUREMENT OF FILM PRODUCT SPREAD ONTO HD6 PLATES Roughness of the substrate. The roughness of the HD6 substrate was measured by non- contact surface topographic analysis using an “Altisurf 500” Lab-workstation from Altimet™, France. The system is composed of an optical sensor, a motion controller, an x-y translation stage, and a microtopography software Mountain Altimap module. The confocal optical sensor “Altiprobe” is based on a white light chromatic aberra- tion principle that allows a high resolution: 10 nm vertical and 1 μm horizontal. Five different areas of exactly 10×5 mm were analyzed according to the scheme illustrated in Figure 3. Surface topography parameters. As described in our previous publications (5,14), the control chart enables the roughness of an HD6 surface to be characterized. In the present publication, the control chart of the HD6 substrate with and without C.B. pretreatment was determined. For each covered PMMA plate, fi ve areas were ana- lyzed. We obtained the respective values for the ten parameters for every location, following which we determined the mean of fi ve values obtained for the fi ve different sites studied. Figure 3. Localisation of the fi ve areas measured with an “Altisurf 500” Lab-workstation.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)