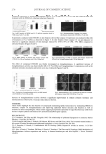
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 250 Figure 4a shows a clear separation of both phases of emulsion A, in contact with the molded plate. After stabilization, it results in multiple non-covered areas the poor cover- age of the surface may explain why the SPF value is lower than the results expected with the fi lters used (Table V). A poor distribution reduces the intensity of the absorption (15). Figure 4b shows that in the presence of C.B. pretreatment, a slight separation of the product phases during spreading on the PMMA is observed by microscopic visualization. After stabilization, it results in a uniform covered area and a good fi lter distribution, which could explain the higher SPF corresponding to the in vivo value. WETTABILITY MEASUREMENTS BETWEEN SAMPLE A AND THE UNTREATED AND PRETREATED HD6 The contact angles between sample A and the HD6 plates were measured with and with- out C.B. The values reported in Table VI signifi cantly decrease in the presence of C.B., refl ecting a better contact between product A and the HD6 PMMA substrate in the presence of the 12-mg C.B. treatment. The C.B. pretreatment improves the attraction of sample A on the PMMA surface, resulting in a better distribution and a higher in vitro SPF. Sample B with good in vitro/vivo correlation. In contrast to sample A, sample B yields results in line with the in vivo value (Table VII) whatever the level of the hydrophilicity of the HD6. MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS In the case of untreated as well as treated PMMA plates, both phases of product B remain homogenous (Figure 5) during the spreading on PMMA. After stabilization, it results in a homogenous fi lm distribution. The distribution of sample B is homogenous in both cases, which explains the similar SPF values. In the case of sample B, the wettability measurements are also in accordance with the in vitro SPF results. In fact, the lowest value of the contact angle measured on an untreated Table V Mean Values of In Vitro SPF for Sunscreen Product A Sample A (in vivo SPF = 16) Untreated PMMA plate PMMA plate + TegoBetain F50 Mean SPF 5.59 18.46 Std. SPF 0.36 1.2 Cov. SPF 6.50% 6.52% Figure 4. (a) Microphotography on untreated HD6. (b) Microphotography on C.B.- treated HD6.
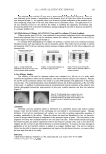
IN VITRO SPF DETERMINATION ON HD6 PMMA 251 PMMA plate is signifi cantly different from the value obtained with sample A. Therefore, the lowest interfacial tension of the interface solid/liquid explains the good wettability of sample B when it’s applied on an untreated PMMA plate (Table VIII). The examination of this value between the sunscreen product and the PMMA surface after C.B. pretreat- ment explains the increase in the homogeneity of the sunscreen and the lower covariance obtained (large decrease in the contact angle). In addition, the fi nding of an SPF value almost equivalent with or without pretreatment for sample B demonstrates that the C.B. fi lm does not affect the microtopography of the substrate and, as a consequence, conforms with the criteria of the control chart. WETABILITY MEASUREMENTS BETWEEN SAMPLE A AND THE UNTREATED AND PRETREATED HD6: EXTENSION OF THE COHORT OF FORMULATIONS The study was extended to 30 sunscreen formulations coming from internal develop- ment, as well as to competitive products, in order to have a wide range of galenic proper- ties. The in vivo SPF value or claimed SPF is known for each formulation. When one considers the protocol without C.B. pretreatment, even if the R2 is low (0.17), the overall Table VI Values of the Contact Angle (θ) between Sunscreen Product A and the Substrate before and after Pretreatment Sample A Untreated HD6 HD6 + C.B. PMMA plate n° 1 63° 45° PMMA plate n° 2 64.4° 47° PMMA plate n° 3 62.8° 51° Mean of the contact angle (θ) 63.4° 47.6° Table VII Mean Values of In Vitro SPF for Sunscreen Product B Sample B (in vivo SPF = 30) Untreated PMMA plate PMMA plate + TegoBetain F50 Mean SPF 35.22 36.91 Std. SPF 3.69 1.17 Cov. SPF 10.49% 3.16% Figure 5. (a) Microphotography on untreated HD6. (b) Microphotography on pre-treated HD6.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)