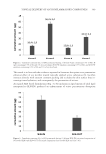
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 334 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION COMPARISON OF THE HYDRATION EFFECTS OF THE TESTED CP AND OINTMENT BASE Skin hydration was measured on pretreated skin, with the period within 24 h of applica- tion selected as a decisive interval for diagnosis of the action. The observed hydration ef- fect for each CP was comparable (Fig. 2): Beline® 12.7 ± 6.5 c.j., Ziaja® 11.9 ± 7.4 c.j., Eucerin® 13.5 ± 7.7 c.j., Allpresan® 13.9 ± 7.2 c.j., DiabeCare® 15.3 ± 7.0 c.j., and Scholl® 16.5 ± 8.3 c.j. In contrast, the value of hydration shown for the ointment base without active hydration ingredients was at the level of pretreated skin. The negative hydration values for Scholl® just after application corresponded to the impenetrable fi lm that it created and the imperfect penetration of the cream into the epidermis. The evi- dence of the occlusive fi lm is shown in Fig. 3. COMPARISON OF TEWL WITHIN THE AREAS OF APPLICATION OF THE CP AND THE OINTMENT BASE The results of TEWL measurement (Fig. 4 Table II) of the untreated control area exhib- ited a slight decrease over the measured time intervals compared with the baseline. When comparing the control area to those with the CP applied, a decrease was shown in TEWL values at the measurement times of 1, 2, 3, 4, 24, and 25 h, i.e., a positive effect of the products used on skin barrier function. The highest negative differences found were those after 4 h of exposure to CP, for Beline®, Ziaja® and DiabeCare® creams, and the Allpresan® foam. As regard the ointment base, the same was found after 4 and 25 h of its action on the skin. The Scholl® cream was found to have increased the TEWL value within 1, 3, and 26 h of action compared to the control surface. Values expressing an occlusive effect of the tested CP were reported only for the Scholl® cream and the ointment base used. For the Figure 2. Corneometric measurements of skin hydration.
MOISTURIZING EFFECT OF TOPICAL COSMETIC PRODUCTS 335 ointment base, the occlusion effect disappeared after 1 h of application to the skin, which for Scholl® occurred after 3 h of the cream’s action. Statistical results from comparing the tested CP with the ointment base at each time interval (signifi cance p ≤ 0.05) were found and identifi ed as * in Table II. COMPARISON OF THE HYDRATION EFFECT OF CP WITH THE DECLARED CONTENT OF 10% UREA Furthermore, two different CPs with the declared content of 10% urea were subject to comparison for the effect of hydration, including Eucerin® and Allpresan®, and investi- gated corneometrically. Both of the products contained other active moisturizing agents. F-tests were carried out to discern the effects of these two products against the control untreated area. For Eucerin®, increased hydration was shown to be signifi cant at time Figure 3. The occlusive fi lm of the Scholl® cream (image captured on a Visioscope). Figure 4. TEWL after the application of CP monitored and the ointment base.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)