JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 394 For the purpose of accuracy, the known amounts of 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde were added to sample solution (recovery test). The procedure of the test comprised the analysis of three different lotion solutions, in four replicates each, which spiked with 0.5, 1.5, and 2.5 μmol and represented the low, me- dium, and high concentrations of the linearity concentration range, respectively. STABILITY OF THE COLOR COMPOUND The preparation of stability test for 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde–Purpald® adduct was conducted. The sample was prepared according to general procedure with spiking of the sample with an appropriate amount of the aldehyde to obtain a solution of 4 × 10−4 mol·l−1 concentration. Afterward, the measurement of the absorbance was executed at room temperature for 90 min. ASSAY HYDROXYISOHEXYL 3-CYCLOHEXENE CARBOXALDEHYDE IN A DOSAGE FORM The procedure for determination of hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde in cosmetic is the same as that described for calibration procedure for 3-cyclohexene-1- carboxaldehyde. One milliliter of lotion was transferred in a test tube, then 1 ml of 0.1 mol·l−1 Purpald® solution and 1 ml of 1 mol·l−1 sodium hydroxide solutions were added. The mixture was left at room temperature for 45 min and then ethanol was added to a volume of 5 ml. Absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 538 nm, against blank test. The blank test was composed of 1 ml lotion and 1 ml of 1 mol·l−1 sodium hydroxide solution. The mixture was also left at room temperature for 45 min and then ethanol was added to a volume of 5 ml. The amount of hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde in lotion was calculated using the regression equation. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In this work, we used the reaction of aldehydes with Purpald®, which is a specifi c reagent for aldehydic group as shown in Figure 2. As a result of reaction of aldehydes with described derivatization reagent purple derivatives are formed. This reaction was taken as a base to develop a spectrophotometric method for determination of cyclohexene-1- carboxaldehyde and hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde. Figure 2. Reaction scheme between Purpald® and carbonyl compounds.
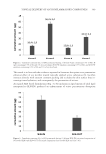
APPLICATION OF PURPALD® FOR DETERMINATION OF CARBOXALDEHYDES 395 OPTIMIZATION OF ANALYTICAL CONDITIONS A wide range of parameters leading to the highest absorbance of the corresponding pur- ple product should be taken into consideration to establish optimum conditions for spec- trophotometric determination of 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehydes. The optimal conditions for the course of reaction of 3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde were established in prelimi- nary tests. The following parameters can be enumerated for exemplifi cation: analytical wavelength optimum reaction time and concentration of sodium hydroxide, Purpald® solutions, and organic solvent. The selected optimal conditions were used to determine different amounts of both compounds and to establish determination ranges for 3-cyclo- hexene-1-carboxaldehyde and hydroxyisohexyl 3-cyclohexene carboxaldehyde. The reaction takes place in an alkaline solution of Purpald® in the presence of oxygen and yields a violet derivative that absorbs most strongly at 538 nm (Figure 3) for both com- pounds. This is caused by identical structure of chromophores (conjugated system) in both derivatives. According to the literature reports (15,19,26), the purple colored prod- ucts of this reaction absorb most strongly in the region of 520–550 nm. The effect of derivatization reaction time on the absorbance value was studied. The maximum intensity was obtained after 45 min of reaction initiation of cyclohexene-1- carboxaldehyde with Purpald® (Figure 4). Several reports have described that in many cases, the time of analysis, which uses Purpald®, ranges from 15 to 25 min (15,21,23,26). The optimal reaction time for the studied aldehydes is 45 min. The structure of aldehyde infl uences this value. The presence of the ring and the double bond causes a higher steric hindrance, which may slow down the reaction of aldehydes with Purpald®. As a result, the time required to obtain maximum absorbance is longer. Figure 3. Absorption spectrum of the colored products (produced from the reaction between Purpald® and determined compounds solutions) and absorption spectrum of used lotion caldehyde = 2.0·10−4 mol·l−1, cPurpald® = 1.0·10−2 mol·l−1.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)