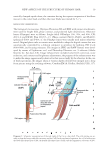
PRACTICAL SELECTING METHOD OF WAVE LOTION FOR HAIR DRESSER 33 EXTENSIONAL SETTING TEST The extensional setting experiments were performed on single hair fi bers in specially devised columns equipped with tensile tester (TENSILON UT-1-4-1, Toyo Baldwin, Tokyo, Japan). The columns are shown in Figure 1, and the experimental procedure is described sche- matically in Figure 2. The procedure of the extensional setting test was basically the same as that used by Wort- mann. However, there were some differences between the two methods. Figure 1. Apparatus used for the extensional permanent treatment. Column A is positioned on the lower jaw of the cross head of the tensile tester. Column B ensures a constant water level in Column A, such that the 20% index can be measured. Then, both columns A and B are combined and fi lled with water.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 34 First, the pretreatment of the hair was different. Wortmann conducted a stress–strain test in water with the hair held in the shape of the desired curve. The hair was then restored to its normal condition and mounted as a loop. Subsequently, the hair was relaxed for 20 min and then extended by 0.5%, after which the reduction/rinse/reoxidation/rinse sequence was initiated. In the present study, after selecting straight hairs and measuring their diameters, the fi bers were extended by 1.5% in water and then the reduction/rinse/ reoxidation/rinse sequence was immediately initiated. In addition, the hairs were not mounted as loops rather, each single hair was exactly fi xed to 120.0 mm as the original length to be extended before being placed in water. Thus, the hairs were not relaxed in water for 20 min followed by reduction with physical relaxation of the hair. The differ- ences in the procedures are due to the fact that in the present study, the aim was to simu- late the actual process used in beauty parlors. Second, the method used to determine the set length during the extensional test was dif- ferent. Wortmann determined the initial extended length and the set length after treat- ment by extrapolating the stress–strain curve to zero. We determined these lengths by direct measurement of the extended and set lengths using a method developed in house (see Step 6: Measurement of the set length). Third, the method for measuring the Young’s modulus of the hairs after treatment was different. Wortmann determined the value of the Young’s modulus using a dynamic method. In the present study, a static method performed under the same conditions as those used to measure the stress in water was employed (see section Step 7: Extension). Prior to the experiments, experimental column and single wet hair fi ber were prepared as described in the following section. Experimental column equipment. Specially designed experimental equipment was used for this study. As can be seen in Figure 1, glass columns A and B were connected via a tube Figure 2. Graphical depiction of the procedure adopted for measuring the extensional permanent treatment. Typical experimental curve obtained for a static extensional permanent treatment.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)