DETERMINATION OF O-PHENYLPHENOL IN SKIN LOTION 131 (0.1 v/v%). The samples were eluted from the column at room temperature at a fl ow rate of 0.5 ml/min. REAGENTS OPP, 2-hydroxyfl uorene as an internal standard (IS), NBD-COCl, methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, isopropyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, butyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, isobutyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, and benzyl 4-hydroxybenzoate were obtained from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Paraben-free skin lotions (A, B, and C) were purchased from a market in Kanazawa city, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. Although OPP was stated to be present on the container labels of skin lotions A and B, the concentration was not given. Other general reagents were obtained from Wako Pure Chemical Industries (Osaka, Japan). PROCEDURES Derivatization. Ultrapure water was from a Milli-Q water purifi cation system (Simplicity® UV Millipore Corporation, Bedford, MA). A standard solution of OPP (2 mg) in methanol (10 ml) was prepared and stocked at 4˚C. Working standard solutions (0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 μg/ml) were prepared by dilution with 10% methanol. Borate buffer (0.1 M) was adjusted to pH 8.5 by the addition of NaOH. Borate buffer (100 μl) was added to a mixture of a diluted standard sample (100 μl) and IS in 0.1% acetonitrile solution (100 μl, 0.1 μg/ml), then NBD-COCl solution in acetonitrile (100 μl, 2 mg/ml) was added. After reaction for 2 min at room temperature, saturated L-aspartate solution (100 μl, fi ltrate of 5 mg/ml of L-aspartate suspension) was added to stop the reaction, and an aliquot (20 μl) of the solution was injected into the HPLC system. Figure 1. Derivatization of OPP and IS with NBD-COCl.
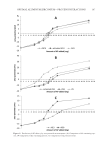
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 132 Sample preparation and addition-recovery tests. Three tested skin lotions (A, 5.0 mg B, 100 mg C, 200 mg) were each diluted to 50 ml with 10% methanol, derivatized, and analyzed as described above. Addition-recovery tests were carried out to assess the accuracy of the method by spiking skin lotion samples with OPP (0.005 mg for A, 0.003 mg for B, 0.003 mg for C). An aliquot of 100 μl was analyzed and the OPP concentration in each sample was determined. Recovery was calculated as follows: Total amount after spiking Spiked amount Original amount Recovery % 100 × RESULTS AND DISCUSSION DERIVATIZATION OF OPP WITH NBD-COCL For the time-course study, the reaction time was set at 1, 2, 3, 5, or 10 min at room tem- perature at various pH values. OPP (100 μl, 0.1 μg/ml), IS solution (100 μl, 0.1 μg/ml), borate buffer (100 μl, various pH values), and NBD-COCl (100 μl, 2 mg/ml) were mixed as described in Experimental. The reaction of OPP at pH 8.5 was faster than under the other pH conditions examined, and the derivatization of OPP reached a maximum at 2 min, but subsequently declined somewhat (Figure 2A). The peak area ratio of NBD-CO- OPP derivative to NBD-CO-IS derivative was most stable at pH 8.5 and 9.0 (Figure 2B). Thus, the derivatization time of 2 min at pH 8.5 was selected. CHROMATOGRAMS Figure 3 shows typical chromatograms obtained from (a) blank spiked with IS and (b) standard sample (0.1 μg/ml) spiked with IS. The retention times of NBD-CO-OPP and Figure 2A. Time courses of formation of NBD-CO-OPP derivative. Standard samples (0.1 μg/mL) were reacted with NBD-COCl in borate buffer at pH 8.0 to 10.0 at room temperature. ( ), pH 8.0 (○), pH 8.5 (□), pH 9.0 ( ), pH 9.5 (×), pH 10.0. Data are expressed as mean values of two experiments. Figure 2B. Time courses of peak area ratio for formation of NBD-CO-OPP and NBD-CO-IS derivatives. Standard sample (0.1 μg/mL) and IS solution (0.1 μg/mL) were reacted with NBD-COCl in borate buffer at pH 8.0 to 10.0 at room temperature. ( ), pH 8.0 (○), pH 8.5 (□), pH 9.0 ( ), pH 9.5 (×), pH 10.0. Data are expressed as mean values of two experiments.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)