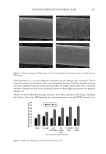
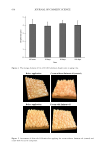
571 ANTI-ACNE PERFORMANCE OF COSMETIC SKINCARE PRODUCTS that the application of “anti-acne cream” produces an important improvement in skin barrier function and skin color. The proportion of the porphyrin area (Figure 2E) and the content of skin surface lipids (Figure 2D) decreases significantly when the skin is treated for 2 weeks, although the content of the lipids shows a slight increase after 4 weeks. The ratio of pore area (Figure 2C) shows a slight increase, and no statistically significant differences are found compared to control groups (p 0.05). CLINICAL ASSESSMENT Acne number. Many types of acne such as open acne, closed acne, papules, pustules, and nodules are classified. The amount of acne can be used to reflect the seriousness of the acne. As shown in Figure 3, the number of open acne (Figure 3A), closed acne (Figure 3B), papules (Figure 3C), and pustules (Figure 3E) display a general reduction after the use of the product. Among these types of acne, a significant decrease of open acne, closed acne, and papules when treated for 2 and 4 weeks is found compared to the control groups (p 0.05). Also, the numbers of pustules show a significant decrease when treated for 4 weeks compared to those before the use of the product (p 0.05). Acne grade and pore rating. As seen in Table I, the acne grade and pore rating of the subjects have significant decreased when treated for 2 and 4 weeks, compared to control groups (p 0.05). The results show that applying the anti-acne product can improve the acne degree of the subjects. Greasy degrees and moist degrees. As seen in Figure 4, the scores of skin grease (Figure 4A) and moisture (Figure 4B) increase significantly when treated for 2 and 4 weeks, compared to the control groups (p 0.05). The higher the skin grease score, the less greasy the skin. The results indicate that applying the product can improve the skin grease and skin moisture. SELF-ASSESSMENT As seen in Figure 5, the scores of greasiness (Figure 5A), pores (Figure 5B), moisture (Figure 5C), and skin comfort (Figure 5D) from all subjects increased significantly when exposed to Figure 1. Visual changes of skin erythema and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation of subjects treated by anti-acne cream (images obtained by VISIA-CR).
Figure 2. Physicochemical indicator. (A) The moisture content of the cuticle. (B) TEWL value. (C) Proportion of pore area. (D) Skin surface lipids. (E) Porphyrin area. (F) A value. “*” indicates that the comparison between data at different time points and base value has statistical significance ( 0.05). 572 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)