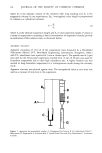
EFFECT OF POLYOXYETHYLENE ON FLOCCULATION 115 increased as the polyoxyethylene chain was lengthened, provided that surfactant concentration was expressed on a molar basis. The effect of surfactant concentration on sedimentation volume of benzocaine suspensions is shown in Figure 5. Sedimentation volume is used as a measure of 0.8i 0,4i I I I •. 20 40 60 concentration (x 104M) Figure 5. Effect of surfactant concentration on sedimentation volume of benzocaine (mean particle size = 2.3/.tm) suspensions. (0) polyoxyethylene (7.5) nonylphenol (•.) polyoxyethylene (15) nonylphenol (,) polyoxyethylene (50) nonylphenol. flocculation state. DeflocCulated suspensions settle to a very small volume and often tend to cake. Flocculated suspensions, which generally are much easier to redisperse, settle to larger sedimentation volumes. Returning to Figure 5, F was quite high at very low surfactant concentrations. These suspensions (at surfactant concentrations below 20 X 10-4M) were poorly wetted, however, and the suspended material contained a great deal of air. As the surfactant concentration was raised, wetting improved and F dropped, reaching a constant value for each surfactant. The concentration of 50 x 10-4M was used for all subsequent experiments with suspensions because, at this concentration, small differences in concentration had no effect on surfactant adsorp- tion (Figure 3) or fiocculation state of suspensions (Figure 5). As the benzocaine suspensions settled, a clear layer of medium separated from a concentrated suspension phase. This mode of settling, usually referred to as subsidence, often occurs in concentrated suspensions. The subsidence of several suspensions over a period of time is shown in Figures 6 and 7. The time axis is logarithmic to span the wide time range studied. Subsidence appears to occur in two stages. During the first stage, which lasted for approximately 5 hr (Figure 6),
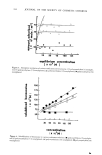
116 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 I I I 10 100 1000 Minutes (log scale) Figure 6. Subsidence of benzocaine suspended in various surfactant solutions. (I) polyoxyethylene (7.5) nonylphenol (•.) polyoxyethylene (15) nonylphenol (E]) polyoxyethylene (50) nonylphenol. 0.6 0.4 I i lO lOO days ( log scale ) Figure 7. Subsidence of benzocaine suspended in various surfactant solutions. (m) polyoxyethylene (7.5) nonlyphenol (•.) polyoxyethylene (15) nonylphenol (E]) polyoxyethylene (50) nonylphenol.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)