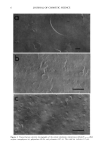
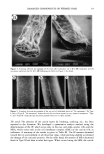
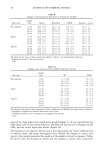
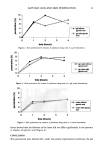
26 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE shows that the presence of glycolic acid significantly decreased the pH of all the der- mocosmetic bases studied. STUDY OF IN VIVO SKIN PENETRATION BY VITAMIN A PALMITATE IN THE FORMULATIONS UNDER STUDY After extracting vitamin A palmitate from the biopsy material, we determined its percentages of penetration as s function of time for the formulations studied. The results are presented in Table III. A test based on the Tukey test indicated that seven animals are sufficient to detect statistically significant differences for the variation determined by analysis of variance. ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To determine the possible presence of statistically significant differences among the formulations studied in terms of vitamin A palmitate penetration into the skin, the data were analyzed by analysis of variance, followed by the Tukey test, which was more adequate for the mathematical model used in the experiment. The results are summa- rized in Tables IV through VII. Time factor, Analysis of variance revealed a significant difference at the 1% level with respect to the times studied in the present investigation, indicating that the time factor strongly affected vitamin A palmirate penetration into the guinea pig skin. The comple- mentary Tukey test for the time factor demonstrated that at time one-hour, penetration was significantly lower than at the other two times studied, which, in turn, did not differ from one another. The results of the Tukey test for the time factor are shown in Ta- ble IV. G/yco/ic acid factor. Analysis of variance showed that there was no significant difference in percent penetration between formulations containing or not containing glycolic acid. Table II pH Values Obtained Formulations pH Gel No additive Vitamin A palmitate added (2%) 70% glycolic acid added (10%) Vitamin A palmitate (2%) + 70% glycolic acid (10%) added Gel cream No additive Vitamin A palmirate added (2%) 70% glycolic acid added (10%) Vitamin A palmirate (2%) + 70% glycolic acid (10%) added Cream No additive Vitamin A palmitate added (2%) 70% glycolic acid added (10%) Vitamin A palmitate (2%) + 70% glycolic acid (10%) added 5.00 5.10 2.70 2.70 5.50 5.90 2.85 2.85 6.00 5.50 2.70 2.70
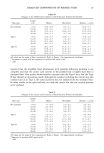
GLYCOLIC ACID AND SKIN PENETRATION 27 Table III Percentages of Applied Dose of Vitamin A Palmitate in the Skin of Guinea Pigs Exposed to the Various Formulations (IU/0.5 cm 2 Guinea Pig Skin) Time (h) Formulation 1 2 4 Gel Without glycolic acid With glycolic acid Gel cream Without glycolic acid With glycolic acid Cream Without glycolic acid With glycolic acid 3.93 5.79 5.02 7.83 5.30 9.12 4.55 6.72 6.59 2.26 6.68 8.37 10.07 5.46 2.88 8.83 6.83 9.39 9.34 9.44 3.30 4.96 8.59 7.92 6.21 7.72 9.55 4.16 7.13 4.77 4.09 5.76 9.91 13.26 4.82 8.07 8.16 10.75 6.82 14.90 4.67 6.83 6.08 4.03 13.23 6.38 6.60 6.12 4.44 5.08 7.41 12.09 6.41 5.74 3.20 4.04 7.66 5.28 11.07 7.83 3.30 4.18 3.24 8.39 5.91 10.11 3.45 5.25 7.78 6.62 4.39 10.01 6.89 8.20 5.81 8.78 7.08 4.95 4.19 5.28 7.53 6.62 5.26 9.22 8.67 4.92 8.25 6.48 8.60 5.72 3.35 3.48 7.57 11.74 5.40 3.41 2.95 7.55 5.51 6.09 7.66 5.69 3.61 6.44 3.23 3.55 4.74 5.58 4.86 3.22 4.72 4.09 3.57 5.26 3.18 3.09 5.64 3.18 5.46 4.09 4.77 4.40 4.43 2.49 7.13 3.39 4.17 2.55 4.03 3.27 6.37 5.47 3.71 2.55 6.91 4.54 5.27 5.13 3.50 3.34 5.62 2.25 6.49 3.38 It should be pointed out that, due to the depilation, there probably was a change in the thickness of the corneal layer of the guinea pig skin. An attempt was made to reduce this error to a minimum by depilating the skin 24 hours before the experiment. Formulation factor. Statistical analysis showed a highly significant difference at the 1% level between formulations in terms of vitamin A palmitate penetration into the skin of Table IV Tukey Test Applied to the Time Factor Data Time (h) Means Critical Tukey value (5%) 1 5.20# 2 6.47* 3 6.39* 1,0524 Means followed by identical symbols are not significantly different.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)