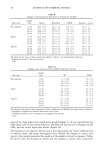
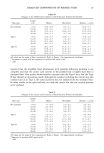
46 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table I: Linear, Logarithmic, Exponential and Power Fits of Perceived Attributes and Complex Viscosity Model Tested A ttrib u te Linear Logarithmic Exponential Power A B A B A B A B Firmness 0.75 -0.52 0.76 -0.49 0.79 -0.58 0.83 -0.57 Stickness 0.64 -0.69 0.61 -0.72 0.49 -081 0.46 -0.81 Peaking, -0.33 -0.34 -0.42 -0.34 -0.22 0.20 -0.31 0.24 Cohesivenes 0.15 -0.54 0.17 -0.64 0.26 -0.20 0.26 -0.29 Wetness -0.81 -0.18 -0.80 -0.14 -0.76 0.46 -0.72 0.48 Thickness 0.89 -0.19 0.88 -0.14 0.89 -0.63 0.92 -0.56 Absorbency -0.67 -0.38 -0.66 -0.40 -0.62 0.26 -0.62 0.24 A m o u n t o f 0.90 -0.12 0.91 -0.06 0.85 -0.66 0.91 -0.57 Residue Spreadability -0.90 -0.14 -0.90 -0.12 -0.92 0.42 -0.89 0.47 Stickiness 0.94 -0.04 0.93 0.06 0.91 -0.59 0.94 -0.32 Gloss 0.93 -0.03 0.94 0.02 0.85 -0.62 0.90 -0.57 Shpperiness -0.70 -0.29 -0.70 -0.29 -0.76 0.27 -0.71 0.29 Liking -0.75 0.04 -0.75 0.11 -0.73 0.53 -0.69 0.60 Absorbency -0.83 -0.14 -0.82 -0.11 -0.83 0.43 -0.80 0.48 Softness -0.88 -0.13 -0.87 `0.10 -0.88 0.45 -0.84 0.49 A: r 2 of perceived attribute vs. oil percentage, B: r 2 of perceived attribute vs. rheological property (Tan(y)*100). Table !!: Three Dimensional Fit of Perceived Attributes and Complex Viscosity Attribute Correlation coefficient Wetness 0.993 Overall Softness 0.978 Amount of residue 0,962 Gloss 0.962 SpreadaNlit¾ 0.958 Stickiness 0.950 Overall Absorbency 0.936 Overall Liking 0.936 Slipperiness 0.768 Thickness 0.756 Absorbency 0.745 Stickiness 0.738 Peaking 0.600 Firmness 0.388 Cohesiveness 0.256
PREPRINTS OF THE 1997 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 47 NEWLY DEVELOPED EMULSIFICATION TECHNOLOGY FOR USE IN HIGHLY EFFICIENT COSMETIC AND SUNSCREEN FORMULATIONS RHEOLOGICAL, MICROSCOPIC AND SUN PROTECTION EFFICIENCY CHARACTERIZATION Liliana S. George, Ph.D., Stepan Company, 22 W. Frontage Rd., Northfield, IL 60093 INTRODUCTION: The aim of the present work was to develop a highly efficient emulsification technology. The technology describes several emulsifying systems for Oil in Water emulsions. The systems are comprised of a non-conventional theology modifier/emulsifier, in combination with a low HLB emulsifier and/or a polymer. The theology modifier/emulsifier also works as a suspending agent by itself The technology is useful in skin care products and sun care products, including creams and lotions for sensitive skin and water resistant SPF sunscreens. CONCLUSIONS: The advantages of the technology are summarized by the following key findings: 1. The emulsifying system, comprised of 2% of the theology modifier/emulsifier and 1% of a low HLB emulsifier (such as Glycerol Monostearate), is very versatile rendering stable emulsions with various oils and active ingredients over a wide range of HLB's (from 5 to 12). 2. The emulsifying system, comprised of 2% of the theology modifier/emulsifier and 1% of a low HLB emulsifier, is very efficient yielding stable oil in water emulsions with total oils emulsified ranging from 7.5% to 45%. 3. The emulsification technology improves the delivery of cosmetically active ingredients, such as sunscreens, silicones, moisturizers and vitamins, resulting in highly efficient formulations. 4. The emulsifying system has a synergistic effect with physical sunscreens and/or water soluble sunscreens in combination with organic sunscreens. 5. The emulsions developed based on this technology are extremely mild and have intrinsic water resistant characteristics, two attributes stemming from the presence of the theology modifier/emulsifier. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: CHARACTERIZATION OF THE RHEOLOGY MODIFIER/EMULSIFIER BASED TECHNOLOGY The theology modifier, the key component of the technology, is the sodium salt of stearyl amidobenzoic acid. Its anionic nature renders activity at the oil/water interface* and its unique theological profile (Fig. 1) renders thixotropy and shear thinning characteristics to the emulsions employing it (Fig.2), eliminating the need for hydrocolloid thickeners. Figure 1: Rheological profile of stearyl amidobenzoic acid sodium salt (slurry in water). Figure 2: Rheological profile of O/W emulsion. Interfacial Tension Measurements recorded on Spinning Drop Tensiometer identified the optimum ratio of the components of the emulsifying system as 2:1, when the sodium salt of stearyl amidobenzoic acid is paired with a low HLB emulsifier. Figure 3 illustrates the interfacial tension reduction recorded for different concentrations of the sodium salt of stearyl amidobenzoic acid at the water/Isopropyl Palmitate interface vs. 0.5% low HLB emulsifier (G!ycerol Monooleate). A ratio of 2:1 of the components of the emulsifying system reduces the IFT of water/IPP below I mN/m.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)