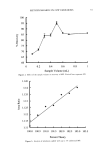
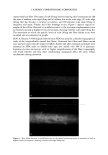
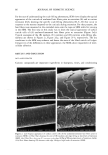
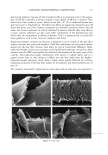
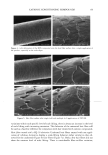
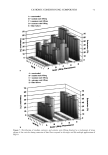
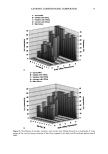
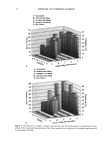
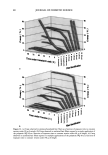
106 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE NOVEL PLANT-DERIVED ANTI-IRRITANTS John J. Wille, Ph.D. Bioderm Technologies, Inc., Trenton, NJ 08608 Introduction Recently, much interest has focused on the use of plant extracts with proven anti-irritant activity [1]. Here, we present results on three different plant-derived anti-irritants: auxins (indole-3- acetic acid, IAA), the isoflavones, quercetin and an onion leaf hydroalcoholic extract [2], and tasselin, a novel hydroalcoholic extract of corn plant tassels. Auxins are well-known plant growth regulator with pleiotropic effects on plant growth, differentiation, and MAP kinase activation [3]. Isoflavones are currently in use as anti-oxidant in cosmetic formulations [4]. In addition, many rayonolds possess epidermal growth factor-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity [5]. Tasselin has good anti-irritant potential for cosmetic applications. Material and Methods Indole-3-acetic acid, phenoxyacetic acid, quercetin dihydrate, and phenoxyacetic acid methyl ester were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co (St. Louis, MO). Sampie preparation and characterization: Between 10-100 grams wet weight of either onion leaves or corn tassels were extracted overnight by continuous stirring at 22øC with 30 volumes of a 50:50 mixture of 95% ethano!:deionized water. The extract was clarified by low speed centrifugation, and concentrated further by rotary evaporation. Hydroalcoholic extracts were analyzed by a Waters I-WLC using acetonitrile- water mobile phase, a C-18 column with lml/min flow rate, and scanned by UV monitor. In vitro tests: The HaCat line of human keratinocytes (gilt fi-om Dr. Pittelkow, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN) were grown in a serum-fi-ee medium containing various combinations of growth factors to explore extract effects on autocrine driven cell growth. In Vivo tests: Subjects were patch tested for dermal irritation using 20mm diameter Finn chambers and filter pads soaked histamine (0.2%), or histamine plus test anti-irritant plant extracts, attached to volar surface of forearm using Scanpot hypo-allergenic tape and left under occlusion for 24 hours. Signs of erythema (redness) and or edema were noted, and the skin patch areas were examined for alterations in skin hydration (capacitance) with Model 825 Corneometer (Courage& Khazaka, Koln, Germany). Results and Discussion a) auxins: IAA(7xE-5M), but not indole-3-proprionic acid, was moderately inhibitory to HaCat keratinocyte cell growth when added to complete serum-free media supplemented with insulin and EGF. Figure I shows that 1% auxix(A) combined with histamine(Hist+A) significantly(s)reduced skin hydration due to occlusion of intact skin with histamine only ('Hist), a known skin irritant. A similar result was obtained when lactic acid(5%) was combined with IAA. b). isoflavones: Quercetin dihydrate was strongly inhibitory of HaCat cell growth under both exogenous growth factor control (insulin plus EGF) and under autocrine growth control (insulin plus retinol acetate). Figure 2 shows that quercetin inhibits autocrine growth, which we have shown to be under MAP/ERK signaling thru studies on PD135035, a specific inhibitor of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. c) onion leaf extracts(OLE): semi-purified hydroalcoholic extracts prepared fi'om onion leaf gave absorption profiles in both the visible and ultra-violet wavelengths compatible with those for purified isoflavones. When OLE was added to a growing culture of HaCat keratinocytes, autocrine growth control was profoundly inhibited. d) tasselin: semi-purified hydroalcoholic extracts were re-taken up in methanol and examined by HPLC chromatography. 96% of the total material eluted as four distinct peaks with elution times(minutes) of 7.52(26%), 8.25(43%), 8.55(16%), and 9.4(11%), respectively. Authentic samples ofphenoxyacetic acid (PA) and phenoxyacetic acid methyl ester (PAME) when mixed at equivalent 50:50 mixture eluted between 7.5-8.2 and 9.2-10.9, respectively. Tasselin preparations spiked with PA and PAME co-eluted with authentic PA/PAME peaks, and had similar UV-absorption spectra. Previously, we reported that PAME and PA were good anti-irritants in the mouse ear swelling test [6]. Tasselin preparations were potent inhibitors of HaCat growth (Figure 3A), and displayed significant (s) anti-irritant activity by blocking histamine-induced elevated skin hydration (Hist+T) (Figure 3B). Conclusion. A plant growth factor, auxin, and hydroalcoholic extracts of onion leaf and corn tassels were found to have good anti-irritant activity.
2002 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 107 Figure I •o ß o Figure 2. Effect of Topical Auxin on Histamine- Induced Elevated Skin Moisture ] ß . 20 0 O eo 120 Post-Occlusion AlrEx suro(m In) Figure 3A. Eftact mm n • u • rowth Figure 3B. Effect of Tasselin on Histamine4nduced Skin Moisture of Intact Skin under 24h-Occlusion • v•h . s p•st-Occlusi•n (rain) • • [1] A.Kydonieus and J. Wiile in:Biochemical Modulation of Skin Reactions, pp. 205-217, 2000. A. Kydonieus and J. Wille, eds. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. [2] K. MockaRis and S. Howell. The Plant Journal, 24:785-796, 2001 [3] K. Miean and S. Mohamed. J. ,4gricult. & Food Chem., 49:3105-3112, 2001 [4] S. Gupta. Happi 38(7): 56-61, 2001. [5]. U. Wenzel et al. J Pharm. & Exptl. Therapeut. 299:351-357, 2001. [6] J. Wiile et al. Skin Pharm. & Skin PhysJol., 13:65-74, 2000.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)