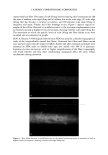
24 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Differences in levels of DNA were determined by carrying our paired t-tests using the JMP statistical package (SAS Institute Inc.) for the before-and-after coloring and when comparing root and tip levels of DNA from the same switch. LOCALIZATION OF DNA IN HAIR SHAFTS Approximately 20 hairs, 1.5 cm in length, were randomly cut from hair switches. These cut lengths were stained for 2 h at room temperature in 10 pM of TOTO-3 © (double stranded DNA-specific stain from Molecular Probes). After washing, the stained hair samples were immediately embedded in Agar 100 epoxy resin, and polymerized overnight at 60øC. Thin 4-1am cross sections were then cut using a Histo diamond knife. These sections were mounted in water on glass microscope slides and gently heated in order to optimally fiatten the mounted sections. For microscope examination, the dry fiat resin-embedded hair sections were mounted in glycerol, cover slipped, and finally sealed with nail varnish. Hair sections were also cut first and the staining carried out afterwards in the same way. All hair sections were examined using a computerized Olympus Provis AX microscope equipped with brightfield, differential interference contrast, and epi-illumination fluo- rescence observation modes. In order to observe cuticle detail, an auxiliary x2 zoom lens and a x5 projection eyepiece were used. The fluorescence filter assembly suitable for TOTO-3 © was obtained from Omega Optical. Unstained hair sections were almost completely dark, indicating negligible hair autofluorescence backgrounds. Thus all significant fluorescence intensities measured in this work relate solely to TOTO-3 © fluorescence emission and were background-free. RESULTS IDENTIFICATION OF DNA FROM HAIR SHAFTS The Pico-green © assay of the DNA extracted from hair confirmed the presence of double-stranded DNA. From a single hair, approximately 0.4 ng of DNA was extracted. From 0.2 g of hair, the amount of DNA extracted was between 12 ng and 50 ng. Variation in levels of DNA was seen between different hairs from the same head, as well as between individuals, but DNA was always present. PCR products were clearly visible for three of the samples of DNA extracted from hair for the HLA-DQA1 locus, giving a product of 241 bp. Very low concentrations of DNA and samples that had not been subjected to a cleanup column did not amplify. A gel showing the successful amplification for the HLA-DQA1 gene is shown in Figure 1. EFFECTS OF COLORING AND WASHING ON LEVELS OF SHAFT DNA Levels of DNA were significantly reduced after permanent colorant treatment of hair. Mean (+standard deviation): before treatment 0.94 + 1.53 ng DNA/mg hair vs after treatment 0.74 + 1.08 ng DNA/mg hair, p 0.05, n = 18.
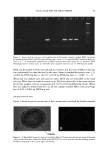
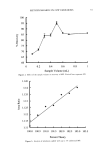
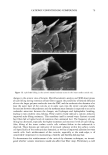
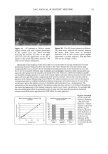
DNA ANALYSIS OF HAIR FIBERS 25 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Fi• ,•rc 1. Ag•,u• g•l •l,uwi,,g •utt•sful amplification of the human leukocyte antlgen DQA 1 genotype for human genomic DNA and DNA extracted from hair. Lanes 1, 6, 9: amplified DNA extracted from hair. Lanes 2-5, 7, 8: Unsuccessful amplification of DNA extracted from hair. Lanes 10, 11: Genomic DNA (Promega) positive controls. Lane 12: TE buffer alone negative control. Lane 13:100 base pair ladder. DNA was detectable in both root-end and tip-end hair, but the level of DNA in the tips was considerably less than the level in the roots. Mean (+standard deviation): roots 1.31 (+0.84) ng DNA/mg hair vs tips 0.3 (+0.64) ng DNA/mg hair, p 0.007, n = 11. When hair was washed once, five and ten times, DNA was not detectable in the wash solution. When hair was washed twenty times, DNA was detectable in the wash solution for all four samples, with an average loss of 0.1325 (+0.03) ng DNA/mg of hair. When hair was soaked in diluted base for 2 h, all four samples leached DNA, with an average loss of 0.24 (+0.06) ng DNA/mg hair. LOCALIZATION OF DNA Figure 2 shows a typical cross section of hair, stained and visualized for double-stranded Cuticle Figure 2. A. Bright field image of a cross-sectioned hair fiber. B. Fluorescence microscopy image of the same cross-sectioned hair fiber, stained for DNA using TOTO-3 ©. It can be seen that the area showing presence of DNA corresponds to the cuticle region of the hair.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)