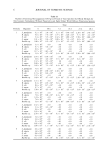
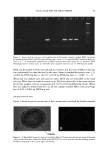
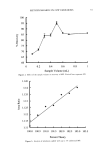
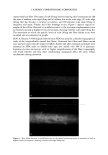
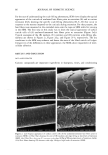
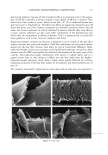
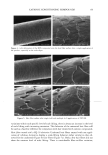
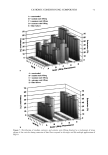
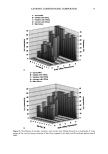
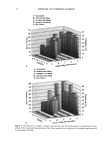
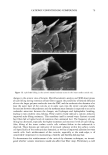
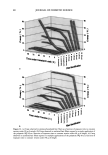
66 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE For the ease of understanding the scale-lifting phenomena, SEM views display the typical appearance of the cuticula of unaltered hair fibers prior to extension (A) and at various extension levels showing the specific scale-lifting phenomena (B, C, D) that occur in response to the stresses imposed on the cuticula during extension. For that purpose, the hair fibers were mounted in the extended state onto the tape on SEM stubs for viewing in the SEM. The first step in this study was to show the typical appearance of surface cuticle cells of (A) unaltered/untreated hair fibers prior to extension (Figure 2a,b). Typical examples of the (B) random, (C) common and (D) extreme scale-lifting phe- nomena are shown in Figure 2c, Figure 2d,e, and Figure 2f h, respectively. The dry conditions in the SEM may enhance and freeze the state of the lifted cuticle cell edges. Irrespective of the differences in their appearance, the SEMs show impairment of inter- cellular adhesion. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION MCCs AND KERATIN Cationic compounds are important ingredients in shampoos, rinses, and conditioning '70e007 5.0 kV b60803 ß ... •. c•eaeas s.e ,v xee•' '•i•' •s. d•eaeas s.e ,v x•.eik"•e:•' •s, Figure 2. (a,b) Typical appearance of surface cuticle cells of (A) un•tered/untreated hair fibers prior to extension (SEM). (c) Hair fiber showing the start of (B) random scale edge li•ing at low levels of extension (gEM). (•,e) Ilaie •bce• sho, i,• (C)tun .... on •tale edge 1if•g at •ermediate •eveis or' extension (f-h) Hair fibers showing (D) extreme scale edge lifting at high levels of extension (SEM).
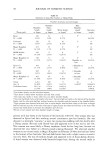
CATIONIC CONDITIONING COMPOUNDS 67 and styling products, because of their beneficial effects in grooming and in the appear- ance of the hair assembly. Cationics display a high degree of affinity to keratin. Hair fibers have a low isoelectric point, which is near pH 3.67 (2) in unaltered human hair and even lower in bleached hair. Therefore, hair fibers are negatively charged at any pH above this point, and since cosmetic treatments are normally carried out above this pH value, the cationic polymers are readily adsorbed by keratin. Besides their own affinity to hair, cationic polymers can also cause other components of the formulations into which they are incorporated to adhere to keratin. This is a property that is utilized by many products, such as the "leave-on" products and rinses. Interaction between cationics and keratin is believed to occur mainly at the hair fiber surface, and only low-molecular-weight (-1000 Da) conditioners are expected to diffuse deeper into the hair fiber interior, most likely by way of intercellular diffusion. High- molecular-weight cationics are not expected to significantly penetrate, except for a short distance into the CMC and possibly the endocuticular domains of the outer layer of the cuticula. Low-molecular-weight conditioners were shown to adsorb faster and to a greater extent (due to their ability to diffuse into the hair shaft) than the highest- molecular-weight polymers, which show a rapid initial uptake followed by leveling, indicating saturation of the hair fiber surface by the polymer and limited penetration, if any (3). The cationics restricted to deposition at scale edges and on scale faces are expected to 60•038 5.0 kV Figure 2. Continued.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)