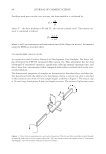
Table III Physicochemical Parameters Formulation codes pH Non-volatile (%) Acid value Saponifi cation value Viscosity cps Thermal stability (%) Microbial count (cfu g)-1 Erythemal score Bc0 5.4 ± 0.03 20.2 ± 0.6 7.0 ± 0.6 40 ± 1 5000 ± 10 97.20 ± 0.6 30 ± 2 0 Cc1 5.8 ± 0.01 21.5 ± 0.2 5.6 ± 0.1 52 ± 2 5500 ± 15 98 ± 0.3 31 ± 1 0 Cc2 6.2 ± 0.03 21.8 ± 0.1 5.8 ± 0.3 50 ± 1 5700 ± 11 98 ± 0.2 33 ± 2 0 Cc3 5.9 ± 0.00 23.5 ± 0.4 8.9 ± 0.2 40 ± 2 5900 ± 10 95 ± 0.1 40 ± 3 0–1 Ac1 5.4 ± 0.02 20.8 ± 0.3 6.2 ± 0.6 42 ± 1 5200 ± 15 97.8 ± 0.6 32 ± 1 0 Ac2 5.2 ± 0.02 21.1 ± 0.3 6.2 ± 0.5 48 ± 1 5500 ± 20 97.9 ± 0.2 35 ± 3 0 Ac3 5.2 ± 0.08 22.9 ± 0.5 10.2 ± 0.4 40 ± 0 5800 ± 10 95 ± 0.6 44 ± 1 0–1 Kc1 4.2 ± 0.05 20.8 ± 0.7 7.8 ± 0.6 42 ± 1 5000 ± 12 97.9 ± 0.3 32 ± 1 0 Kc2 4.8 ± 0.01 21.3 ± 0.9 7.2 ± 0.7 42 ± 3 5500 ± 10 98 ± 0.1 31 ± 4 0 Kc3 4.8 ± 0.04 23.8 ± 0.5 11.1 ± 0.6 40 ± 2 5700 ± 15 94 ± 0.6 42 ± 2 0–1 Tc1 5.6 ± 0.03 21.1 ± 0.6 5.8 ± 0.5 52 ± 1 5200 ± 10 98 ± 0.4 31 ± 1 0 Tc2 5.6 ± 0.02 21.8 ± 0.2 6.0 ± 0.1 50 ± 1 5000 ± 20 98 ± 0.5 37 ± 3 0 Tc3 5.1 ± 0.01 23.5 ± 0.3 9.0 ± 0.3 42 ± 2 5900 ± 10 95 ± 0.6 40 ± l 0–1 Hc1 5.2 ± 0.03 20.5 ± 0.6 6.2 ± 0.6 48 ± 1 5500 ± 10 98.2 ± 0.1 32 ± 1 0 Hc2 5.6 ± 0.05 21.0 ± 0.1 6.0 ± 0.5 48 ± 2 5700 ± 20 98 ± 0.3 35 ± 1 0 Hc3 5.1 ± 0.01 22.9 ± 0.3 9.2 ± 0.3 40 ± 2 5900 ± 10 95 ± 0.6 40 ± 2 0–1 p value 0.10 0.10 0.0086 0.0014 0.10 0.0001 0.0743 All values are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3) p 0.01 shows no signifi cant differences, while p 0.01 shows signifi cant differences between the observed data of the same column. HERBAL FORMULATIONS FOR SKIN IMPROVEMENT 125
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 126 Figure 1. In vitro sun protection factor determination of herbal formulations with codes given below: Bc0= base cream. Cc1, Cc2, Cc3= creams with 1%, 3%, and 5% Cinnamon extracts. Ac1, Ac2, Ac3= creams with 1%, 3%, and 5% Areca extracts. Kc1, Kc2, Kc3= creams with 1%, 3%, and 5% Curcuma extracts. Tc1, Tc2, Tc3= creams with 1%, 3%, and 5% Tamarindus extracts. Hc1, Hc2, Hc3= creams with 1%, 3%, and 5% Centella extracts. Statistical analysis showed signifi cant differences between base cream values and herbal for- mulation values (p 0.001). effect (R9) were reduced. In absolute parameters, total deformation (Uf) and retraction (Ur) were improved. Elastic deformation (Ue) and viscoelasticity (Uv) were reduced (Tables IV, V). All the physiologically positive results were found signifi cant (p 0.05) when the data of the herbal formulations were compared with the data of the base cream and control, which shows that the extracts penetrated the skin along with the base cream and that they improved skin characteristics. Comparison of the values of the base cream (Bc0) with the baseline, i.e., without formulation (Cc0), produced nonsignifi cant changes (ns p 0.05). The comparative study of ten formulations showed that the formulation of Cinnamon (Cc1, Cc2), Centella (Hc1, Hc2), and Tamarindus (Tc1, Tc2) gave highly signifi - cant results (p 0.001) regarding deformation, retraction, elastic deformation, and visco- elasticity in contrast to the formulation of Areca (Ac1, Ac2) and Curcuma (Kc1, Kc2) (ns p 0.05). On increasing the percent of extract of the same herb, the value was less signifi - cant (p 0.01), but comparison with different extracts gave highly signifi cant results (p 0.001). Long exposure to UV radiation reduces production of collagen in the dermis and the skin loses elasticity. Skin sags and wrinkles are formed due to the thinning of subcutaneous fat and the loss of elasticity. The number of blood vessels, capillaries, sweat glands, and the moisture content of human skin decrease with skin aging. In hydration, sebum and melanin determination of the formulations of all the herbal formulations gave highly signifi cant results results (p 0.001) as compared to the base cream (Bc0). The results showed that Cc1, Cc2, Tc1, Tc2, Hc1, and Hc2 had increased skin hydration, sebum levels and decreased melanin values after four weeks and were more effective than Ac1, Ac2, Kc1 and Kc2 (Figures 2–4). The results revealed that for Cc1, Cc2, Hc1, Hc2, Tc1, and Tc2 showed remarkable improve- ments in biomechanical and electrical properties, which is due to the effects of the active constituents (polyphenols and glycosides) present in the hydroethanolic extracts of selected herbs that have reported antioxidant, anti-elastase, antiproliferative, photochemoprotec- tive, antipyretic, anti-allergic, astringent, facemask-toning, and anti-aging properties.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)