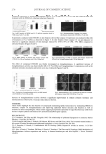
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 228 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ANTI-TYROSINASE ACTIVITY OF GRAPE EXTRACTS L-dopa is an endogenous phenolic substrate for polyphenol oxidase in apple and potato sources (16). It is an intermediate product during oxidation of L-tyrosine and is used commonly as an enzyme substrate of tyrosinase, a polyphenol oxidase (1,9–11,17). In this study, the inhibitory effects of ethanol extracts from peels and seeds of Kyoho grapes and Red Globe grapes (KG-PEE, KG-SEE, RGG-PEE, and RGG-SEE, respectively) toward mushroom tyrosinase activity were evaluated. Therefore, L-dopa was used as the substrate of mushroom tyrosinase to screen the inhibitory activities of ethanol extracts from the grapes. The inhibitory effect of KG-PEE on mushroom tyrosinase activity depended on the concentrations (Figure 1). As the concentrations of KG-PEE increased from 0 mg/ml to 5 mg/ml, the absorbance of OD475nm, an index of dopachrome formation, decreased accordingly, indicating a decrease in tyrosinase activity. All the ethanol extracts showed anti-tyrosinase activity, with the following order: RGG-SEE KG-SEE KG-PEE RGG-PEE. It was noted that the seed extracts from both the Kyoho grapes and Red Globe grapes had higher anti-tyrosinase activities than the peel extracts. To evaluate the inhibitory mechanism of the ethanol extracts, mushroom tyrosinase activ- ity was determined under various L-dopa concentrations. It was found that the reaction rate of tyrosinase decreased as the concentrations of KG-SEE increased from 0.33 mg/ml to 5 mg/ml (Figure 2). KG-PEE, RGG-PEE, and RGG-SEE also reduced the tyrosinase reaction rate in different magnitudes (data not shown). The Lineweaver-Burk plots re- vealed that these extracts served as mix-type inhibitors, and a represented plot for KG- SEE is shown in Figure 3. Figure 1. Relative inhibitory effect of grape extracts on mushroom tyrosinase activity using L-dopa (0.33 mg/ml) as the substrate. Mushroom tyrosinase (44 units/ml) reacted at room temperature for 10 min. Symbols: - - (KG-PEE) - - (KG-SEE) -▲- (RGG-PEE) -×- (RGG-SEE).
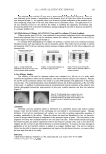
ANTI-TYROSINASE ACTIVITY OF ETHANOL FROM GRAPES 229 THE EFFECT OF PHENOLIC COMPOUNDS We suspected that phenolic compounds played important roles in anti-tyrosinase activity. Thus, the total phenolic content in the ethanol extracts from Kyoho grapes and Red Globe grapes was determined and presented as the amount of gallic acid equivalent. The total phenolic content in KG-SEE and RGG-SEE was 400±11 and 339±7 mg gallic acid equivalent/g, respectively, while KG-PEE and RGG-PEE showed 18±1 and 27±0 mg Figure 2. Michaelis-Menton equation of V versus [ S ] with KG-SEE and L-dopa. The enzymatic assay was performed with mushroom tyrosinase (44 units/ml) at room temperature for 10 min. Symbols: - - (0 mg/ml KG-SEE) - - (0.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -▲- (1.67 mg/ml KG-SEE) -×- (3.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -∗- (5 mg/ml KG-SEE). Figure 3. Lineweaver-Burk plot of 1/V versus 1/[ S ] with KG-SEE and L-dopa. The enzymatic assay was reformed with mushroom tyrosinase (44 mg/ml) at room temperature for 10 min. Symbols: - - (0 mg/ml KG-SEE) - - (0.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -▲- (1.67 mg/ml KG-SEE) -×- (3.33 mg/ml KG-SEE) -∗- (5 mg/ml KG-SEE).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)