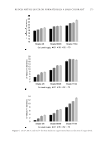
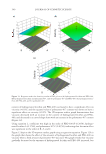
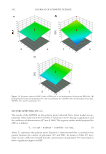
showed a drastic decrease with an interaction effect of hydrogenated lecithin and PEG-400. Figure 12B presents the effect of the content of hydrogenated lecithin and poloxamer 407 on viscosity when a fi xed amount of PEG-400 was used. In this graph, viscosity exhibited a gradual decrease as the amount of hydrogenated lecithin increased, and then maintained constant after a gradual increase as poloxamer 407 content increased. Figure 12C is the graph that demonstrates the effect of the content of poloxamer 407 and PEG-400 on viscos- ity when a fi xed amount of hydrogenated lecithin was used. In this graph, viscosity fi rst showed a small increase and then it decreased with increasing poloxamer 407 concentration. Viscosity exhibited a drastic decrease as the concentration of PEG-400 showed an increase. To sum up the previous outcomes, the content of PEG-400 was found to have the most signifi cant infl uence on viscosity, followed by hydrogenated lecithin. The content of polox- amer 407 alone seemed to have almost no impact, but had an infl uence to some extent in association with the other two compositions. Figure 12. Response surface for viscosity results of PLO gels as (A) hydrogenated lecithin and PEG-400, (B) hydrogenated lecithin and poloxamer 407, and (C) poloxamer 407 and PEG-400. (A) hydrogenated lecithin, (B) PEG-400, and (C) poloxamer 407. PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF PLURONIC LECITHIN ORGANOGELS 341
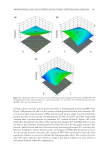
Figure 13. Response surface for DSC results of PLO gels as (A) hydrogenated lecithin and PEG-400, (B) hydrogenated lecithin and poloxamer 407, and (C) poloxamer 407 and PEG-400. (A) hydrogenated lecithin, (B) PEG-400, and (C): poloxamer 407. FACTORS AF FECTING DSC (Y3) The result s of the ANOVA on the gelation point indicated that a linear model was ap- propriate. The p value was 0.0107 ( 0.05) F value was 5.6237, having a signifi cance and the coeffi cient of determination (R2) was 0.5648. The response surface model proposed for DSC is as follows: 3 = 0.5124 + 0.0649 – 0.0047 + 0.1316C, Y A B (3) wh ere Y3 r epresents the gelation point. Equation 3 demonstrated that a correlation was present between the content of poloxamer 407 and DSC. As shown in Table VI, the p value of each coeffi cient revealed that the concentration of poloxamer 407 was found to have a signifi cant impact on DSC. JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 342
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)