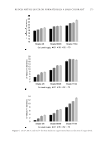
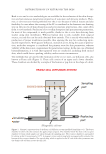
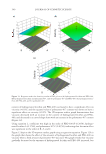
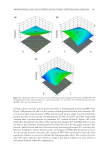
In conclusion, the stability of PLO gel has to be maintained without phase separation at low temperature, room temperature, and constant temperature to evaluate the suitability of PLO gel as a cosmetic ingredient. In particular, stability has to be maintained without fl owability at cold temperatures. Moreover, because excessively high viscoelasticity may infl uence the texture and application of the formulation when spreading it on the skin, the formulation with adequate viscoelasticity seems to be most appropriate. Based on the previous fi ndings, the formulation #2–3 is suggested as the most suitable PLO gel in cosmetic formulations. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Th is research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) through the Encouragement Program for The Industries of Economic Cooperation Region (P0002162). REFERENCES (1) H. E. Jin, J. H . Kim, and I. Y. Paik, Transdermal drug delivery system, J. Korean Ind. Eng. Chem., 16(1), 15–20 (2005). (2) B. W. Barry, D r ug delivery routes in skin: a novel approach. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 54, 31–40 (2002). (3) S. Saha, R. Sh i varajakumar, and V. Karri, Pluronic lecithin organogels: an effective topical and transder- mal, ISJPRS, 9(11), 4540–4550 (2018). (4) J. Hadgraft an d M. E. Lane, Skin permeation: the years of enlightenment. Int. J. Pharm., 305(1–2), 2–11 (2005). (5) M. Foldvari, N o n-invasive administration of drugs through the skin: challenges in delivery system de- sign. PSST, 3(12) 417–425 (2000). (6) H. C. Ansel, P h armaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems, N. G. Popovich and L. V. Al- len, Eds. (Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, PA, 1995), 357. (7) J. Franckum, D . Ramsay, N. G. Das, and S. K. Das, Pluronic lecithin organogel for local delivery of anti-infl ammatory drugs, Int. J. Pharm. Comp., 8(2), 101–105 (2004). (8) R. Kumar and O . P. Katare, Lecithin organogels as a potential phospholipid-structured system for topical drug delivery: a review, AAPS PharmSciTech, 6(2), 299–310 (2005). (9) M. Pandey, V. B elgamwar, S. Ganttani, S. Surana, and A. Tekade, Pluronic lecithin organogel as a topi- cal drug delivery, Drug Deliv., 17(1), 38–47 (2010). (10) V. S. Belgamw a r, M. S. Pdney, D. S. Chauk, and S. J. Surana, Pluronic lecithin organogel, Asian J. Pharm., 2(3), 134–138 (2008). (11) S. Murdan, A r eview of pluronic lecithin organogel as a topical and transdermal drug delivery system, Hosp. Pharm., 12, 267–270 (2005). (12) P. Terech and R. G. Weiss, Low molecular mass gelators of organic liquids and the properties of their gels, Chem. Rev., 97(8), 3133–3159 (1997). (13) K. E. Hill, P . C. Mills, B. R. Jones, C. F. Bolwell, D. Aberdein, and J. P. Chambers, Percutaneous ab- sorption of methimazole: an in vitro study of the absorption pharmacokinetics for two different vehicles, J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther., 38(6), 616–618 (2015). (14) A. S. Hickey and N. A. Peppas, Mesh size and diffusive characteristics of semicrystalline poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes prepared by freezing/thawing techniques, J. Membr. Sci., 107, 229–237 (1995). (15) M. M. Adbel-Mottaleb, N. D. Mortada, A. A. Elshamy, and G. A. Awad, Preparation and evaluation of fl uconazole gels, Egypt. J. Biomed. Sci., 23(1), 266–286 (2007). (16) H. Almeida, M. H. Amaral, P. Lobão, and J. M. S. Lobo, Pluronic F-127 and pluronic lecithin organogel (PLO gel): main features and their applications in topical and transdermal administration of drugs, J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 15(4), 592–605 (2012). ( 17) C. L. Esposito, P. Kirilov, and V. G. Roullin, Organogels, promising drug delivery systems: an update of state-of-the-art and recent applications, J. Control. Release, 271, 1–20 (2018). PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF PLURONIC LECITHIN ORGANOGELS 345
( 18) G. Schwarz, Basic kinetics of binding and incorporation with supramolecular aggregates, Biophys. Chem., 26(2–3), 163–169 (1987). ( 19) S. Abrol, A. Trehan, and O. P. Katare, Formulation, Characterization, and in vitro evaluation of silyma- rin-loaded lipid microspheres, Drug Deliv., 11(3), 185–191 (2004). ( 20) P. K. Sharma, M. J. Reilly, D. N. Jones, P. M. Robinson, and S. R. Bhatia, The effect of pharmaceuticals on the nanoscale structure of PEO–PPO–PEO micelles, Colloids Surf. B, 61(1), 53–60 (2008). ( 21) Y. M. Kim and H. C. Moon, Stimuli-responsive smart electrochemical devices based on functional ion gels, Polym. Sci. Techn., 31(1), 14–18 (2020). ( 22) E. S. Gil and S. M. Hudson, Stimuli-responsive polymers and their bioconjugates, Prog. Polym. Sci., 29, 1173–1222 (2004). ( 23) X. J. Ju, R. Xie, L. Yang, and L. Y. Chu, Biodegradable ‘intelligent’ materials in response to physical stimuli for biomedical applications, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat., 19(4), 493–497 (2009). ( 24) N. G. Ran and W. J. Kim, Thermo-responsive polymers for gene delivery, Biomater. Res., 14(2), 86–94 (2010). ( 25) A. R. Islmail, D. Rusli, and A. H. Hazimah, Effect of glycerol derived co-surfactant on the ternary phase behaviour of palm-based microemulsions, J. Oil Palm Res., 26(3), 240–250 (2014). ( 26) S. J. Yoo, J. H. Lee, C. Y. Kim, C. H. Kim, J. W. Shin, H. S. Kim, and J. G. Kim, Direct observation of the crystal structure changes in the MgxZn1-xOalloy system, Thin Solid Films, 588, 50–55 (2015). (2 7 ) I. M. Yang, G. T. Oh, C. B. Yu, and I. G. Hwang, Design and Analysis of Experiments (Minyoungsa, Seoul, Korea, 2015), 432-433. (28 ) V. Litvinenko, Topical Issues of Rational Use of Natural Resources, Vol. 2 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2019), 884. (29 ) C. C. Vidyasagar and Y. A. Naik, Surfactant (PEG 400) effects on crystallinity of ZnO nanoparticles, Arab. J. Chem., 9(4), 507–510 (2016). (3 0 ) A. Dahal, Assessment of the percutaneous absorption of ABH PLO gel across porcine ear skin (Master of Science Thesis, The University of Toledo, Toledo, Spain, 2018). (3 1 ) B. H Jones and T. P. Lodge, Nanocasting nanoporous inorganic and organic materials from polymeric bicontinuous microemulsion templates, Polym. J., 44, 131–146 (2012). (3 2 ) F. S. Bates, W. W. Maurer, P. M. Lipic, M. A. Hillmyer, K. Almdal, K. Mortensen, G. H. Fredrickson, and T. P. Lodge, Polymeric bicontinuous microemulsions, Phys. Rev. Lett., 79(5), 849–852 (1994). (3 3 ) H. J. Kim, T. K. Jeong, J. Y. Kim, and K. S. Yoon, Stabilization of nanoemulsion using PEG-free sur- factant, J. Korean Appl. Sci. Tech., 36(2), 444–457 (2019). JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 346
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)