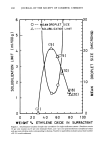
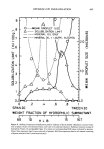
COSMETIC PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES 451 Run One Run Two Fraction Left sector Right sector 1,000-5,000 0.15 ml 0.25 M NaC1 0.15 ml 2 mg/ml protein in 0.25 M NaC1 Temperature 13.00øC Speed Overspeed 52,000 rpm-4 h 44,000 rpm-3 h Equilibrium speed 44,000 rpm-18 h 30,000 rpm- 18 h 5,000-30,000 0.15 ml 0.25 M NaC1 0.12 ml 2 mg/ml protein in 0.25 M NaC1 13.00øC The molecular weights determined by ultracentrifugation were compared to the results obtained by gel filtration as will be shown later in this paper. RESULTS GEL FILTRATION From the elution diagrams (absorbance versus elution volume) of each of the three hydrolysates studied, graphs of molecular weight versus per cent by weight were drawn. These graphs represent the molecular weight distribution curves for these pro- teins. The elution diagrams, Fig. 1, are curves generated by the continuous flow spec- trophotometer. These diagrams are used in preparing molecular weight distribution curves. The enzyme hydrolysate was preserved with methylparabens and propylparabens, as well as benzalkonium chloride. These materials absorb at 280 nm and were eluted from e Enzyme Hydrolysate //•I!• ,,' .,,,\ '• 0 VT 0½13 Acid Hydrolysate ! v T Steam Hydrolysate • I Elution Volumes Figure 1. Elution diagrams, Sephadex G-75 V T
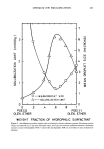
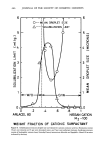
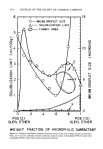
452 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6' 0.4' uclease A 13,700 0.3 %Chymotrypsinogen A 25,000 t 0 1 Ibumin 45,000 I Aldolase 158,000 lX103 lX104 lX10 s Molecular Weight Fiõure 2. Calibration curve, G-?5 lX10 s 20- 18- 14- 12- 8- m Enzyme Hydrolysate ß ,.m.• Acid Hydrolysate • Steam Hydrolysate 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Molecular Weight X 103 Figure 3. Molecular weight distribution curves 26 28 30
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)