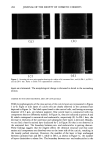
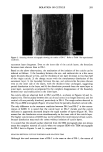
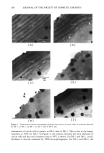
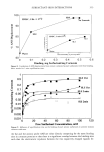
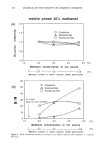
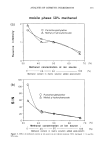
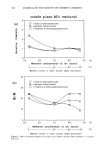
SURFACTANT-SKIN INTERACTIONS 303 containing primarily sodium salts of tallow (a mixture of stearic and palmitic) and coco (primarily lauric) fatty acid. These bars have significantly different mildness character- istics. This was evident from the results of the flex wash (10), soap chamber test (15), and zein dissolution test (7) described in Table II. The flex wash and soap chamber tests are reproducible clinical tests that have been used to distinguish the relative irritancy potential of various soaps and synthetic detergent bars. The results of the zein dissolu- tion test (7) given in Table II are also consistent with the flex wash results and indicate the different mildness characteristics of the three bars. Note that the higher the zein dissolution is, the higher is the irritation potential of the surfactant towards skin (7). Electrophoresis purity-grade sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) was purchased from Bio- Rad Laboratories (Richmond, CA). Sodium laurate was purchased from Eastman Chemical Company (Rochester, NY). Sodium lauroyl isethionate (SLI CH3(CH2)1oCOO(CH2)2SO •-Na +) and •4C labeled SLI were synthesized at Unilever 14 ß - ß Research. C labeled launc ac•d was obtained from Amersham International. The skin irritation tendencies of SLS, SLI, and TEA-Na laurate, as determined by the zein dissolution technique, follow the order: TEA-laurate SLS SLI (see Table III). Potassium hydrogen phthalate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (Aldrich Chemical), and sodium borate (Fisher Scientific) were used for buffer preparations. The fluorescence probes 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonic acid (1,8-ANS) *high purity* (Figure 1A) and fluorescein (Figure lB) were obtained from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR). Full-thickness human skin was obtained from the International Institute for the Ad- vancement of Medicine (Exton, PA). Stratum corneum was isolated by incubating strips of skin, dermis side down, into a solution of 0.5 % trypsin in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at pH 7.4 for 2-4 hours at 37øC. The dermis was separated from the epidermis using forceps, and the latter was incubated in fresh trypsin-PBS solution overnight at 4øC. The enzyme solution was changed several times on the following day before the stratum corneum was washed with agitation and three changes of PBS solution to remove trypsin and residual cells. The stratum corneum was then spread on spectra mesh to dry overnight under desiccation. Full-thickness porcine back skins from 3-4-week-old white albino piglets were obtained from Buckshire Corp. (Perkasie, PA). After the hair from the specimen was clipped and the underlying subcutaneous tissues were removed, the skin was dermatomed to a thickness of approximately 450-500 Table II End Point Erythema Scores in In Vivo Flex Wash (10), Zein Dissolution Results, and Irritation Scores in Soap Chamber Tests (15) for Various Bars Mean total Soap chamber erythema score test-irritation Bar (10) % Zein dissolution* scores (15) BarA 5.7 -+ 1.2 55% 0.5 Bar B 20.4** 79% 2.8 Bar C 27.7 + 2.0** 82% 2.8 * 1% Surfactant active in the test solution. ** Significantly different (p 0.05) from Bar A.
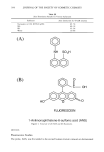
304 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table III Zein Dissolution Results for Various Surfactants Surfactant Zein dissolution by 40-mM solution Na-laurate in 0.04 M TEA (pH9) 85.7% SLS 80.1% SLI 62.2% Water 10.0% (A) so aH (B) i OH FLUORESCEIN 1-Anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonic acid (ANS) Figure l. Structure of (A) ANS and (B) fluorescein. METHODS Fluorescence Studies The probe, ANS, was first added to the excised human stratum corneum or dermatomed
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)