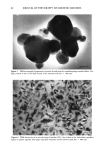
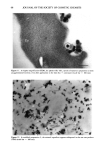
DYNAMIC HAIRSPRAY ANALYSIS 77 1.0 to1.1 cmwide• l [ I •1.5 in. J Overhead view of tress Texture Analyzer Acrylic Probe - 2.5 cm •'{ Hair Shaped into Omega Loop 0.4 cm Down 4 cm calibration height 1,4 to 1,6 cm Up 4 cm calibration height 1,0 mm penetration after 2.0 G L Figure 2. Scheme showing the geometry of hair samples shaped into omega loops. deposited amount (0.15 g of a hairspray solution at 5.71% w/w polymer concentration) was uniformly distributed over the tress surface, thoroughly saturating the fibers be- tween the plastic tabs. The drying process of wet loops was found to be critical to obtain reproducible results. While 100% alcohol-based compositions were found to dry on hair without distorting the original, omega-shaped configuration, other systems containing water produced significant change in the shape of the loop by extending it in the vertical direction. As a result, the tresses increased in height by a few millimeters, and the new shape proved to be unstable in subsequent stiffness measurements, which involved the application of much higher forces than in the case of untreated hair. Typically, an oblong omega loop would be characterized by a high compression force if its symmet- rical shape produced an even distribution of stress and deformation, and conversely, a significantly smaller force if distorted in an unsymmetrical fashion. To preserve the original shape of untreated hair, teflon-coated cylindrical rods were inserted into the loops immediately after treatment. This prevented them from changing their shape as a result of water absorption. The loops were dried and conditioned overnight in an atmosphere of 50% RH and 70øF prior to measurements by the texture analyzer.
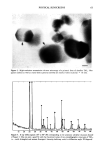
78 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS POLYMERS Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (International Specialty Products) samples were commercial products characterized by the following weight average molecular weights: PVP K15, 8100 PVP K30, 57500 PVP K60, 400000 and PVP K90, 1270000. Ethyl ester of PVM/MA copolymer, butyl ester of PVM/MA copolymer, vinyl caprolactam/PVP/ dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer, and acrylates copolymer were commercial products sold under the tradenames of Gantrez ES 225 (ISP), Gantrez ES 425 (ISP), Gaffix (ISP), and Luvimer (BASF), respectively. "Hard hold" and "soft hold" formu- lations, characterized by the stiffness data presented in Figure 5, were commercial products based on ethyl ester of PVM/MA copolymer or octylacrylamide/acrylates/ butylaminoethyl methacrylate copolymer. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ANALYSIS OF HAIRSPRAY DRYING AT AMBIENT CONDITIONS Figure 3 shows a typical hairspray drying curve in which the force (G) (peak force) is plotted as a function of time. The variation of the geometrical dimensions of a loop is described by the plot of the differential tress height as a function of time (upper curve and the right-hand y axis). The initial portion of each drying curve corresponds to untreated hair. After the assessment of unmodified hair as a reference point, the fibers were sprayed for two seconds, followed by intermittent measurements of stiffness and 0.5 Stiffness •.• 40 of • untreated • hair 0 Differential Tress Height Increase -- ø0.5 - Pointof.Hai.rspray • 60 • Aplhcafiøn •• S6ffness -- -1 -- -1.$ 0 • Tack Duration •--• Maximum Stickiness -20 _ • Total Dry Time -40 I , -3.5 0 1 2 Thousands Time (sec) Fiõur½ 3. Force and diffcrcntia| tress height as • •u•cdo• o•ry]• dmc •o• • •ypic•[ h•irspr•y composition
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)